| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
A graph, like a picture, is worth a thousand words. Graphs not only contain numerical information; they also reveal relationships between physical quantities. This section uses graphs of displacement, velocity, and acceleration versus time to illustrate one-dimensional kinematics.
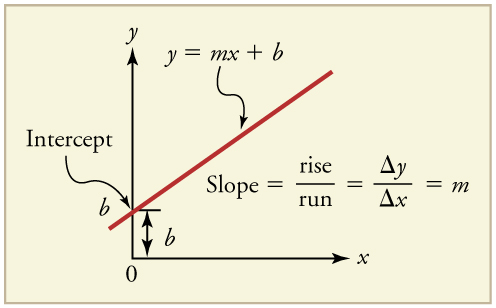
First note that graphs in this text have perpendicular axes, one horizontal and the other vertical. When two physical quantities are plotted against one another in such a graph, the horizontal axis is usually considered to be an independent variable and the vertical axis a dependent variable . If we call the horizontal axis the -axis and the vertical axis the -axis, as in [link] , a straight-line graph has the general form
Here is the slope , defined to be the rise divided by the run (as seen in the figure) of the straight line. The letter is used for the y -intercept , which is the point at which the line crosses the vertical axis.
Time is usually an independent variable that other quantities, such as displacement, depend upon. A graph of displacement versus time would, thus, have on the vertical axis and on the horizontal axis. [link] is just such a straight-line graph. It shows a graph of displacement versus time for a jet-powered car on a very flat dry lake bed in Nevada.
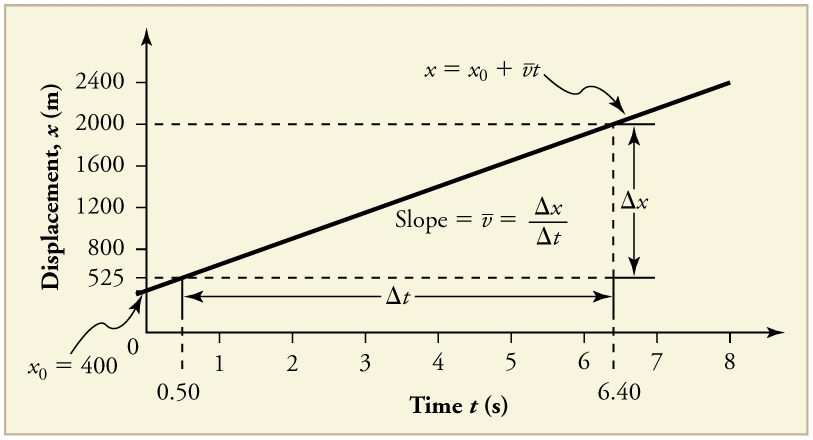
Using the relationship between dependent and independent variables, we see that the slope in the graph above is average velocity and the intercept is displacement at time zero—that is, . Substituting these symbols into gives
or
Thus a graph of displacement versus time gives a general relationship among displacement, velocity, and time, as well as giving detailed numerical information about a specific situation.
The slope of the graph of displacement vs. time is velocity .
Notice that this equation is the same as that derived algebraically from other motion equations in Motion Equations for Constant Acceleration in One Dimension .
From the figure we can see that the car has a displacement of 400 m at time 0.650 m at = 1.0 s, and so on. Its displacement at times other than those listed in the table can be read from the graph; furthermore, information about its velocity and acceleration can also be obtained from the graph.
Find the average velocity of the car whose position is graphed in [link] .
Strategy
The slope of a graph of vs. is average velocity, since slope equals rise over run. In this case, rise = change in displacement and run = change in time, so that
Since the slope is constant here, any two points on the graph can be used to find the slope. (Generally speaking, it is most accurate to use two widely separated points on the straight line. This is because any error in reading data from the graph is proportionally smaller if the interval is larger.)
Solution
1. Choose two points on the line. In this case, we choose the points labeled on the graph: (6.4 s, 2000 m) and (0.50 s, 525 m). (Note, however, that you could choose any two points.)
2. Substitute the and values of the chosen points into the equation. Remember in calculating change we always use final value minus initial value.
yielding
Discussion
This is an impressively large land speed (900 km/h, or about 560 mi/h): much greater than the typical highway speed limit of 60 mi/h (27 m/s or 96 km/h), but considerably shy of the record of 343 m/s (1234 km/h or 766 mi/h) set in 1997.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?