| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If such a galvanometer has a resistance, then a voltage of only produces a full-scale reading. By connecting resistors to this galvanometer in different ways, you can use it as either a voltmeter or ammeter that can measure a broad range of voltages or currents.
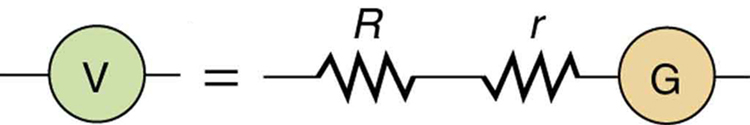
[link] shows how a galvanometer can be used as a voltmeter by connecting it in series with a large resistance, . The value of the resistance is determined by the maximum voltage to be measured. Suppose you want 10 V to produce a full-scale deflection of a voltmeter containing a galvanometer with a sensitivity. Then 10 V applied to the meter must produce a current of . The total resistance must be
( is so large that the galvanometer resistance, , is nearly negligible.) Note that 5 V applied to this voltmeter produces a half-scale deflection by producing a current through the meter, and so the voltmeter’s reading is proportional to voltage as desired.
This voltmeter would not be useful for voltages less than about half a volt, because the meter deflection would be small and difficult to read accurately. For other voltage ranges, other resistances are placed in series with the galvanometer. Many meters have a choice of scales. That choice involves switching an appropriate resistance into series with the galvanometer.
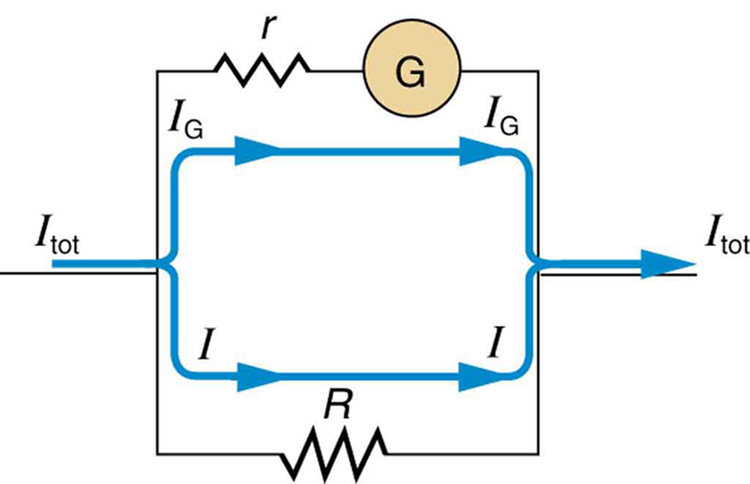
The same galvanometer can also be made into an ammeter by placing it in parallel with a small resistance , often called the shunt resistance , as shown in [link] . Since the shunt resistance is small, most of the current passes through it, allowing an ammeter to measure currents much greater than those producing a full-scale deflection of the galvanometer.
Suppose, for example, an ammeter is needed that gives a full-scale deflection for 1.0 A, and contains the same galvanometer with its sensitivity. Since and are in parallel, the voltage across them is the same.
These drops are so that . Solving for , and noting that is and is 0.999950 A, we have

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?