| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

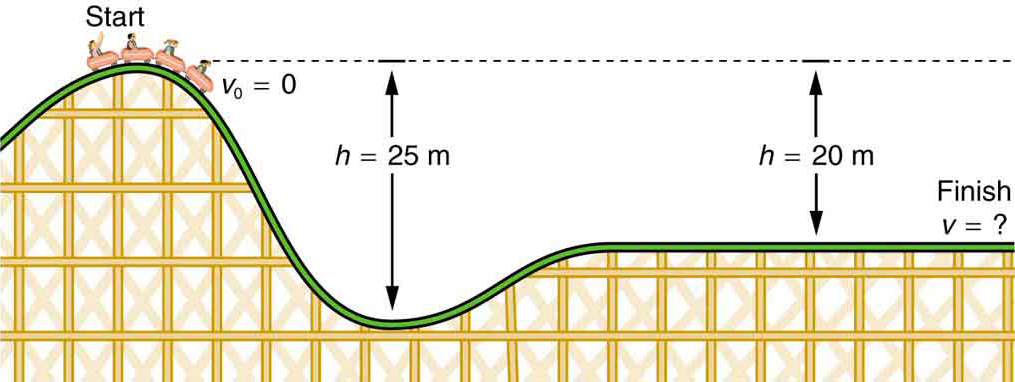
(a) What is the final speed of the roller coaster shown in [link] if it starts from rest at the top of the 20.0 m hill and work done by frictional forces is negligible? (b) What is its final speed (again assuming negligible friction) if its initial speed is 5.00 m/s?
Strategy
The roller coaster loses potential energy as it goes downhill. We neglect friction, so that the remaining force exerted by the track is the normal force, which is perpendicular to the direction of motion and does no work. The net work on the roller coaster is then done by gravity alone. The loss of gravitational potential energy from moving downward through a distance equals the gain in kinetic energy. This can be written in equation form as . Using the equations for and , we can solve for the final speed , which is the desired quantity.
Solution for (a)
Here the initial kinetic energy is zero, so that . The equation for change in potential energy states that . Since is negative in this case, we will rewrite this as to show the minus sign clearly. Thus,
becomes
Solving for , we find that mass cancels and that
Substituting known values,
Solution for (b)
Again . In this case there is initial kinetic energy, so . Thus,
Rearranging gives
This means that the final kinetic energy is the sum of the initial kinetic energy and the gravitational potential energy. Mass again cancels, and
This equation is very similar to the kinematics equation , but it is more general—the kinematics equation is valid only for constant acceleration, whereas our equation above is valid for any path regardless of whether the object moves with a constant acceleration. Now, substituting known values gives
Discussion and Implications
First, note that mass cancels. This is quite consistent with observations made in Falling Objects that all objects fall at the same rate if friction is negligible. Second, only the speed of the roller coaster is considered; there is no information about its direction at any point. This reveals another general truth. When friction is negligible, the speed of a falling body depends only on its initial speed and height, and not on its mass or the path taken. For example, the roller coaster will have the same final speed whether it falls 20.0 m straight down or takes a more complicated path like the one in the figure. Third, and perhaps unexpectedly, the final speed in part (b) is greater than in part (a), but by far less than 5.00 m/s. Finally, note that speed can be found at any height along the way by simply using the appropriate value of at the point of interest.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?