| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As the process continues, the charge separation reverses and the field reaches its maximum downward value, returns to zero, and rises to its maximum upward value at the end of one complete cycle. The outgoing wave has an amplitude proportional to the maximum separation of charge. Its wavelength is proportional to the period of the oscillation and, hence, is smaller for short periods or high frequencies. (As usual, wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional.)
Following Ampere’s law, current in the antenna produces a magnetic field, as shown in [link] . The relationship between and is shown at one instant in [link] (a). As the current varies, the magnetic field varies in magnitude and direction.
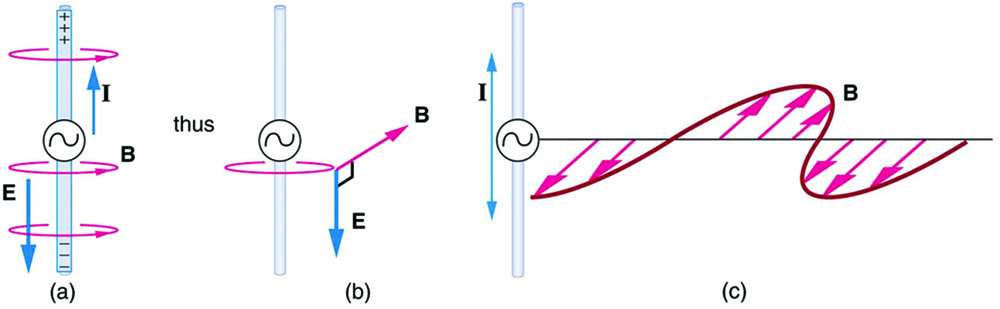
The magnetic field lines also propagate away from the antenna at the speed of light, forming the other part of the electromagnetic wave, as seen in [link] (b). The magnetic part of the wave has the same period and wavelength as the electric part, since they are both produced by the same movement and separation of charges in the antenna.
The electric and magnetic waves are shown together at one instant in time in [link] . The electric and magnetic fields produced by a long straight wire antenna are exactly in phase. Note that they are perpendicular to one another and to the direction of propagation, making this a transverse wave .
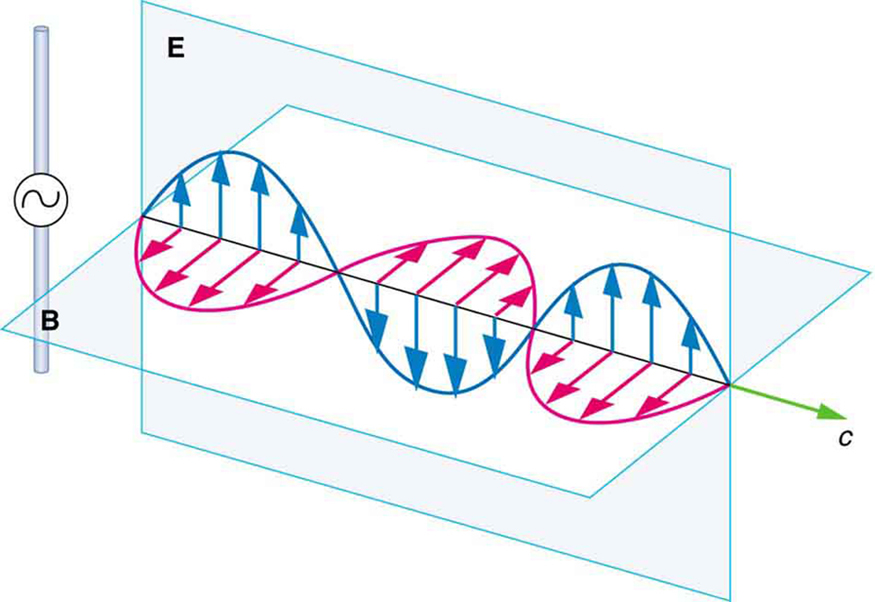
Electromagnetic waves generally propagate out from a source in all directions, sometimes forming a complex radiation pattern. A linear antenna like this one will not radiate parallel to its length, for example. The wave is shown in one direction from the antenna in [link] to illustrate its basic characteristics.
Note that an electromagnetic wave, as shown in [link] , is the result of a changing electric field causing a changing magnetic field, which causes a changing electric field, and so on. Therefore, unlike other waves, an electromagnetic wave is self-propagating, even in a vacuum (empty space). It does not need a medium to travel through. This is unlike mechanical waves, which do need a medium. The classic standing wave on a string, for example, does not exist without the string. Similarly, sound waves travel by molecules colliding with their neighbors. If there is no matter, sound waves cannot travel.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?