| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If the 0.300-mA current through the calculator mentioned in the [link] example is carried by electrons, how many electrons per second pass through it?
Strategy
The current calculated in the previous example was defined for the flow of positive charge. For electrons, the magnitude is the same, but the sign is opposite, .Since each electron has a charge of , we can convert the current in coulombs per second to electrons per second.
Solution
Starting with the definition of current, we have
We divide this by the charge per electron, so that
Discussion
There are so many charged particles moving, even in small currents, that individual charges are not noticed, just as individual water molecules are not noticed in water flow. Even more amazing is that they do not always keep moving forward like soldiers in a parade. Rather they are like a crowd of people with movement in different directions but a general trend to move forward. There are lots of collisions with atoms in the metal wire and, of course, with other electrons.
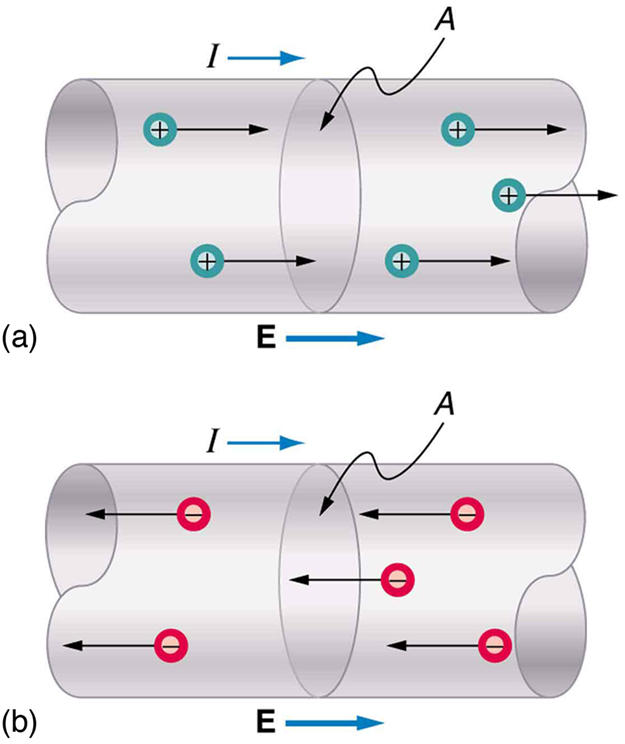
Electrical signals are known to move very rapidly. Telephone conversations carried by currents in wires cover large distances without noticeable delays. Lights come on as soon as a switch is flicked. Most electrical signals carried by currents travel at speeds on the order of , a significant fraction of the speed of light. Interestingly, the individual charges that make up the current move much more slowly on average, typically drifting at speeds on the order of . How do we reconcile these two speeds, and what does it tell us about standard conductors?
The high speed of electrical signals results from the fact that the force between charges acts rapidly at a distance. Thus, when a free charge is forced into a wire, as in [link] , the incoming charge pushes other charges ahead of it, which in turn push on charges farther down the line. The density of charge in a system cannot easily be increased, and so the signal is passed on rapidly. The resulting electrical shock wave moves through the system at nearly the speed of light. To be precise, this rapidly moving signal or shock wave is a rapidly propagating change in electric field.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?