| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Source | Dose (mSv/y) Multiply by 100 to obtain dose in mrem/y. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Australia | Germany | United States | World |
| Natural Radiation - external | ||||
| Cosmic Rays | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.39 |
| Soil, building materials | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.48 |
| Radon gas | 0.90 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 1.2 |
| Natural Radiation - internal | ||||
| 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.29 | |
| Medical&Dental | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.53 | 0.40 |
| TOTAL | 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 2.8 |
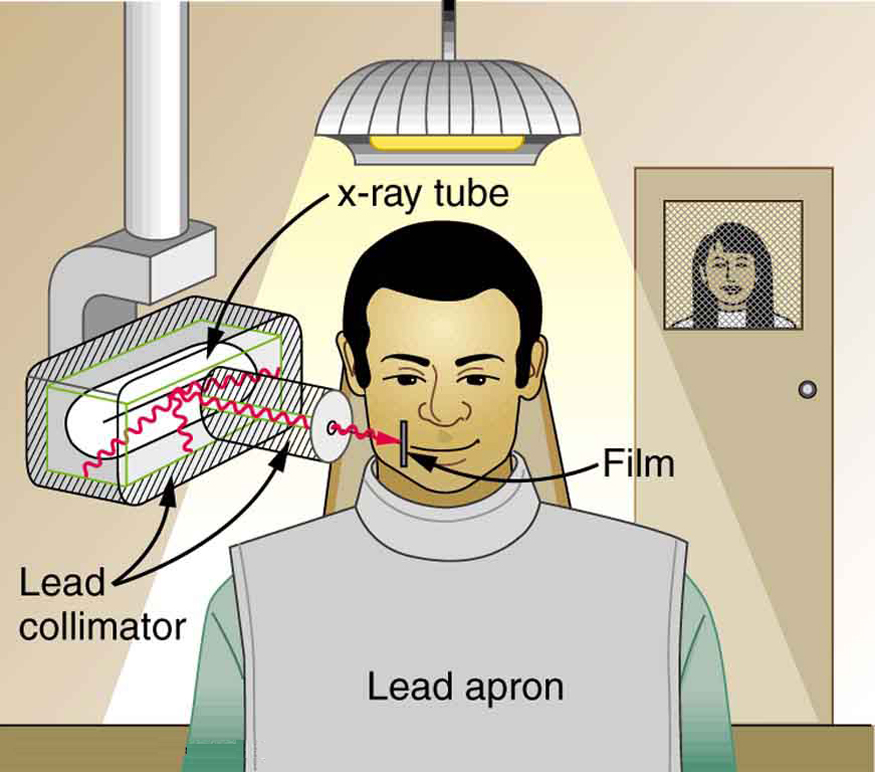
To physically limit radiation doses, we use shielding , increase the distance from a source, and limit the time of exposure .
[link] illustrates how these are used to protect both the patient and the dental technician when an x-ray is taken. Shielding absorbs radiation and can be provided by any material, including sufficient air. The greater the distance from the source, the more the radiation spreads out. The less time a person is exposed to a given source, the smaller is the dose received by the person. Doses from most medical diagnostics have decreased in recent years due to faster films that require less exposure time.
| Procedure | Effective dose (mSv) |
|---|---|
| Chest | 0.02 |
| Dental | 0.01 |
| Skull | 0.07 |
| Leg | 0.02 |
| Mammogram | 0.40 |
| Barium enema | 7.0 |
| Upper GI | 3.0 |
| CT head | 2.0 |
| CT abdomen | 10.0 |
You need to follow certain steps for dose calculations, which are
Step 1. Examine the situation to determine that a person is exposed to ionizing radiation.
Step 2. Identify exactly what needs to be determined in the problem (identify the unknowns). The most straightforward problems ask for a dose calculation.
Step 3. Make a list of what is given or can be inferred from the problem as stated (identify the knowns). Look for information on the type of radiation, the energy per event, the activity, and the mass of tissue affected.
Step 4. For dose calculations, you need to determine the energy deposited. This may take one or more steps, depending on the given information.
Step 5. Divide the deposited energy by the mass of the affected tissue. Use units of joules for energy and kilograms for mass. If a dose in Sv is involved, use the definition that .
Step 6. If a dose in mSv is involved, determine the RBE (QF) of the radiation. Recall that .
Step 7. Check the answer to see if it is reasonable: Does it make sense? The dose should be consistent with the numbers given in the text for diagnostic, occupational, and therapeutic exposures.
Calculate the dose in rem/y for the lungs of a weapons plant employee who inhales and retains an activity of in an accident. The mass of affected lung tissue is 2.00 kg, the plutonium decays by emission of a 5.23-MeV particle, and you may assume the higher value of the RBE for s from [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?