| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The maximum buoyant force is the weight of this much water, or
Discussion
The maximum buoyant force is ten times the weight of the steel, meaning the ship can carry a load nine times its own weight without sinking.
A piece of household aluminum foil is 0.016 mm thick. Use a piece of foil that measures 10 cm by 15 cm. (a) What is the mass of this amount of foil? (b) If the foil is folded to give it four sides, and paper clips or washers are added to this “boat,” what shape of the boat would allow it to hold the most “cargo” when placed in water? Test your prediction.
Density plays a crucial role in Archimedes' principle. The average density of an object is what ultimately determines whether it floats. If its average density is less than that of the surrounding fluid, it will float. This is because the fluid, having a higher density, contains more mass and hence more weight in the same volume. The buoyant force, which equals the weight of the fluid displaced, is thus greater than the weight of the object. Likewise, an object denser than the fluid will sink.
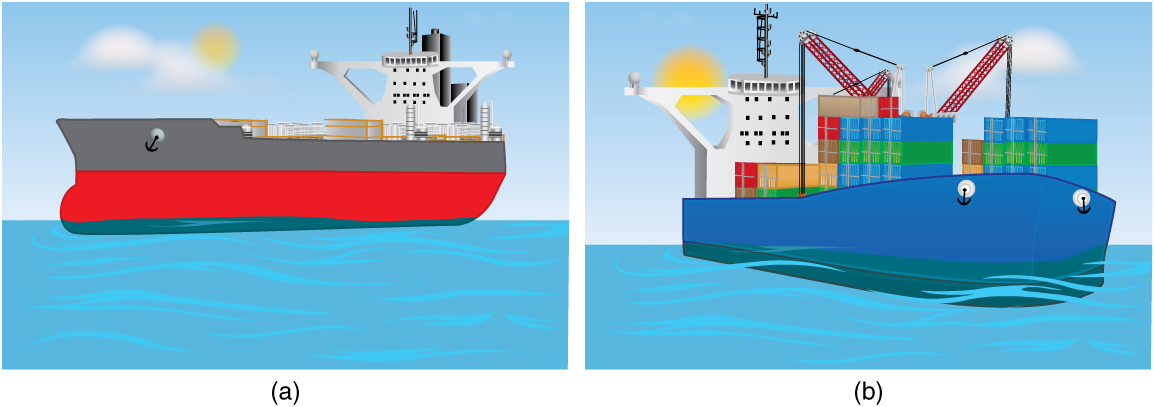
The extent to which a floating object is submerged depends on how the object's density is related to that of the fluid. In [link] , for example, the unloaded ship has a lower density and less of it is submerged compared with the same ship loaded. We can derive a quantitative expression for the fraction submerged by considering density. The fraction submerged is the ratio of the volume submerged to the volume of the object, or
The volume submerged equals the volume of fluid displaced, which we call . Now we can obtain the relationship between the densities by substituting into the expression. This gives
where is the average density of the object and is the density of the fluid. Since the object floats, its mass and that of the displaced fluid are equal, and so they cancel from the equation, leaving
We use this last relationship to measure densities. This is done by measuring the fraction of a floating object that is submerged—for example, with a hydrometer. It is useful to define the ratio of the density of an object to a fluid (usually water) as specific gravity :
where is the average density of the object or substance and is the density of water at 4.00°C. Specific gravity is dimensionless, independent of whatever units are used for . If an object floats, its specific gravity is less than one. If it sinks, its specific gravity is greater than one. Moreover, the fraction of a floating object that is submerged equals its specific gravity. If an object's specific gravity is exactly 1, then it will remain suspended in the fluid, neither sinking nor floating. Scuba divers try to obtain this state so that they can hover in the water. We measure the specific gravity of fluids, such as battery acid, radiator fluid, and urine, as an indicator of their condition. One device for measuring specific gravity is shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?