| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Equally as interesting as the effects of heat transfer on a system are the methods by which this occurs. Whenever there is a temperature difference, heat transfer occurs. Heat transfer may occur rapidly, such as through a cooking pan, or slowly, such as through the walls of a picnic ice chest. We can control rates of heat transfer by choosing materials (such as thick wool clothing for the winter), controlling air movement (such as the use of weather stripping around doors), or by choice of color (such as a white roof to reflect summer sunlight). So many processes involve heat transfer, so that it is hard to imagine a situation where no heat transfer occurs. Yet every process involving heat transfer takes place by only three methods:
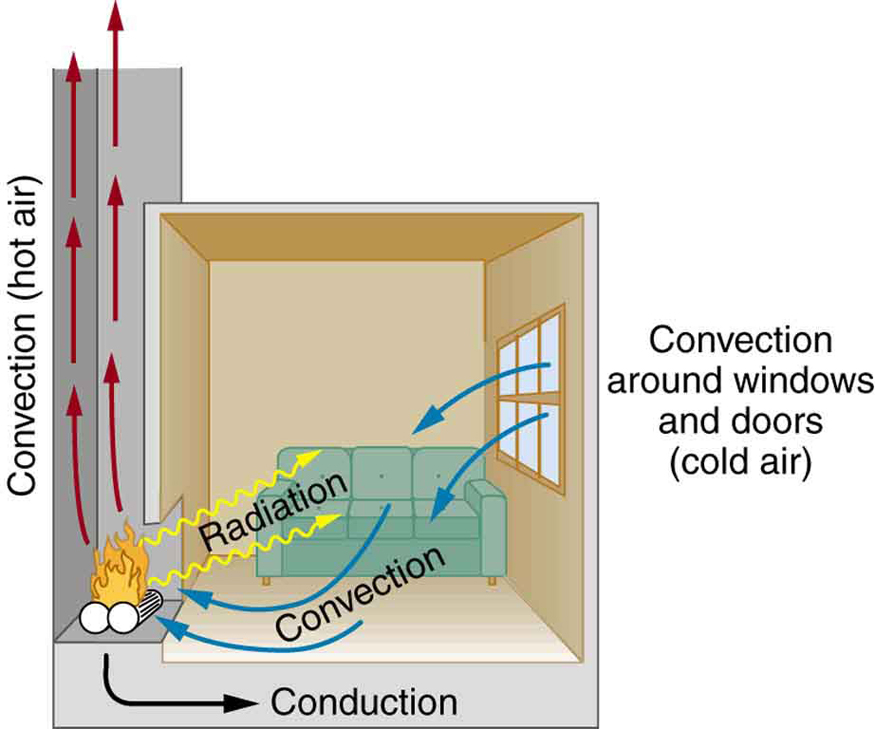
We examine these methods in some detail in the three following modules. Each method has unique and interesting characteristics, but all three do have one thing in common: they transfer heat solely because of a temperature difference [link] .
Name an example from daily life (different from the text) for each mechanism of heat transfer.
Conduction: Heat transfers into your hands as you hold a hot cup of coffee.
Convection: Heat transfers as the barista “steams” cold milk to make hot cocoa .
Radiation: Reheating a cold cup of coffee in a microwave oven.
What are the main methods of heat transfer from the hot core of Earth to its surface? From Earth’s surface to outer space?
When our bodies get too warm, they respond by sweating and increasing blood circulation to the surface to transfer thermal energy away from the core. What effect will this have on a person in a hot tub?
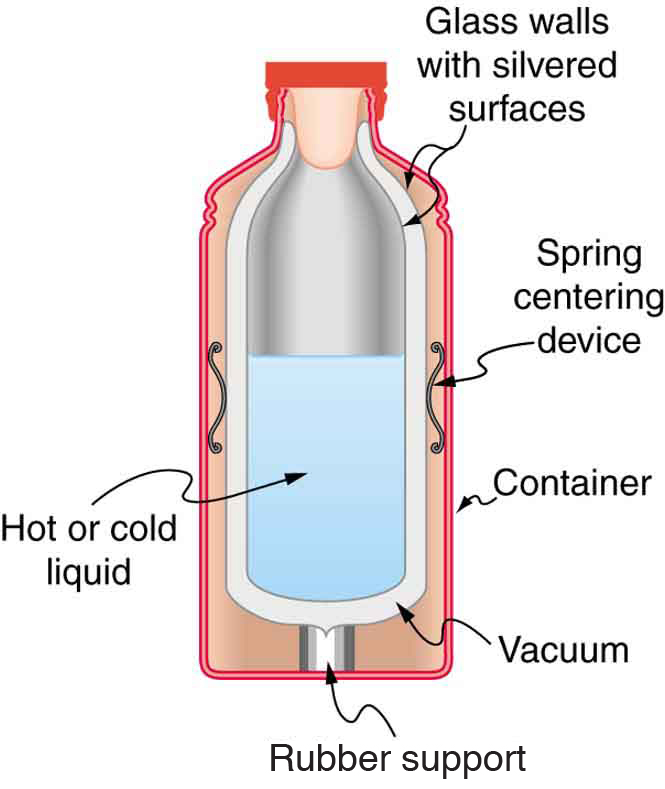
[link] shows a cut-away drawing of a thermos bottle (also known as a Dewar flask), which is a device designed specifically to slow down all forms of heat transfer. Explain the functions of the various parts, such as the vacuum, the silvering of the walls, the thin-walled long glass neck, the rubber support, the air layer, and the stopper.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?