| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
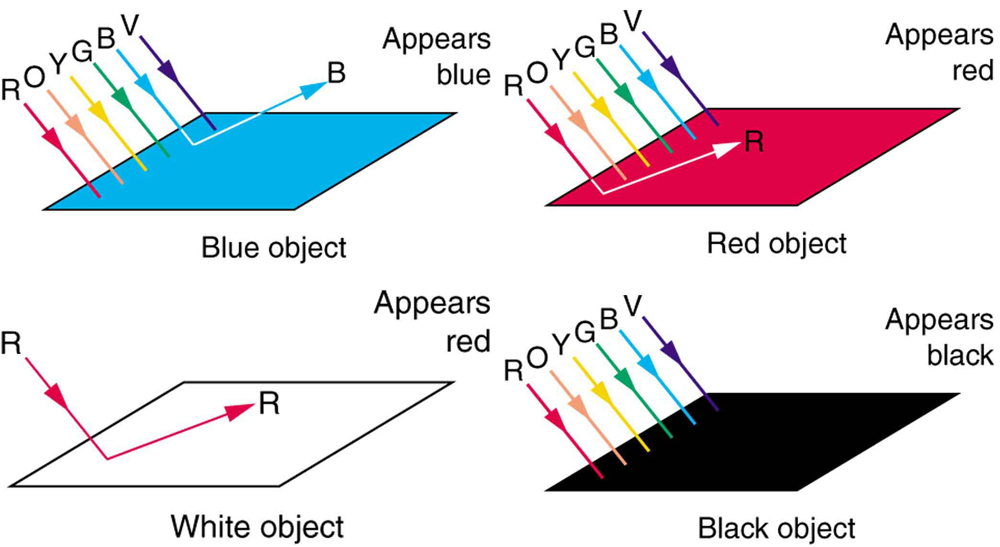
Consider why various objects display color—that is, why are feathers blue and red in a crimson rosella? The true color of an object is defined by its absorptive or reflective characteristics. [link] shows white light falling on three different objects, one pure blue, one pure red, and one black, as well as pure red light falling on a white object. Other hues are created by more complex absorption characteristics. Pink, for example on a galah cockatoo, can be due to weak absorption of all colors except red. An object can appear a different color under non-white illumination. For example, a pure blue object illuminated with pure red light will appear black, because it absorbs all the red light falling on it. But, the true color of the object is blue, which is independent of illumination.
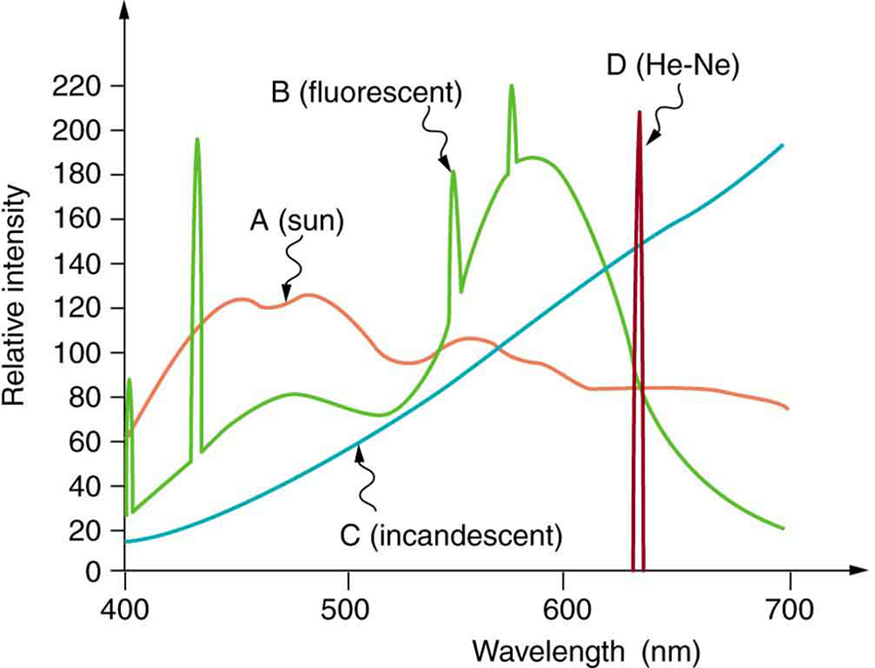
Similarly, light sources have colors that are defined by the wavelengths they produce. A helium-neon laser emits pure red light. In fact, the phrase “pure red light” is defined by having a sharp constrained spectrum, a characteristic of laser light. The Sun produces a broad yellowish spectrum, fluorescent lights emit bluish-white light, and incandescent lights emit reddish-white hues as seen in [link] . As you would expect, you sense these colors when viewing the light source directly or when illuminating a white object with them. All of this fits neatly into the simplified theory that a combination of wavelengths produces various hues.
This activity is best done with plastic sheets of different colors as they allow more light to pass through to our eyes. However, thin sheets of paper and fabric can also be used. Overlay different colors of the material and hold them up to a white light. Using the theory described above, explain the colors you observe. You could also try mixing different crayon colors.
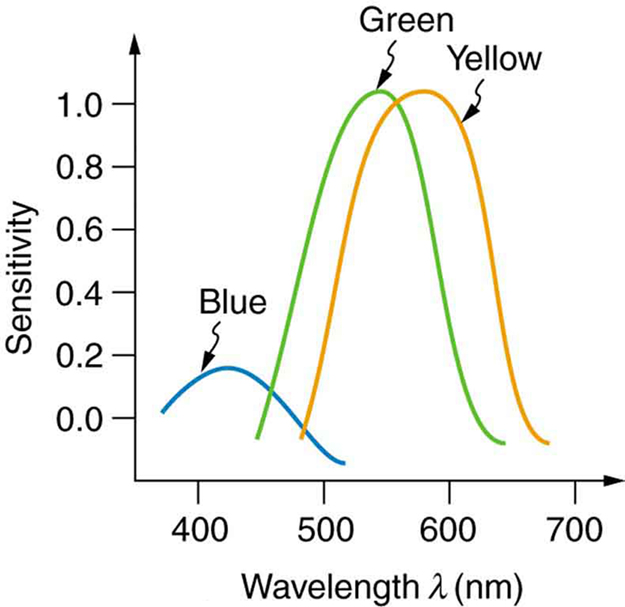
The eye-brain color-sensing system can, by comparing various objects in its view, perceive the true color of an object under varying lighting conditions—an ability that is called color constancy . We can sense that a white tablecloth, for example, is white whether it is illuminated by sunlight, fluorescent light, or candlelight. The wavelengths entering the eye are quite different in each case, as the graphs in [link] imply, but our color vision can detect the true color by comparing the tablecloth with its surroundings.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?