| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(a) Calculate the inductive reactance of a 3.00 mH inductor when 60.0 Hz and 10.0 kHz AC voltages are applied. (b) What is the rms current at each frequency if the applied rms voltage is 120 V?
Strategy
The inductive reactance is found directly from the expression . Once has been found at each frequency, Ohm’s law as stated in the Equation can be used to find the current at each frequency.
Solution for (a)
Entering the frequency and inductance into Equation gives
Similarly, at 10 kHz,
Solution for (b)
The rms current is now found using the version of Ohm’s law in Equation , given the applied rms voltage is 120 V. For the first frequency, this yields
Similarly, at 10 kHz,
Discussion
The inductor reacts very differently at the two different frequencies. At the higher frequency, its reactance is large and the current is small, consistent with how an inductor impedes rapid change. Thus high frequencies are impeded the most. Inductors can be used to filter out high frequencies; for example, a large inductor can be put in series with a sound reproduction system or in series with your home computer to reduce high-frequency sound output from your speakers or high-frequency power spikes into your computer.
Note that although the resistance in the circuit considered is negligible, the AC current is not extremely large because inductive reactance impedes its flow. With AC, there is no time for the current to become extremely large.
Consider the capacitor connected directly to an AC voltage source as shown in [link] . The resistance of a circuit like this can be made so small that it has a negligible effect compared with the capacitor, and so we can assume negligible resistance. Voltage across the capacitor and current are graphed as functions of time in the figure.
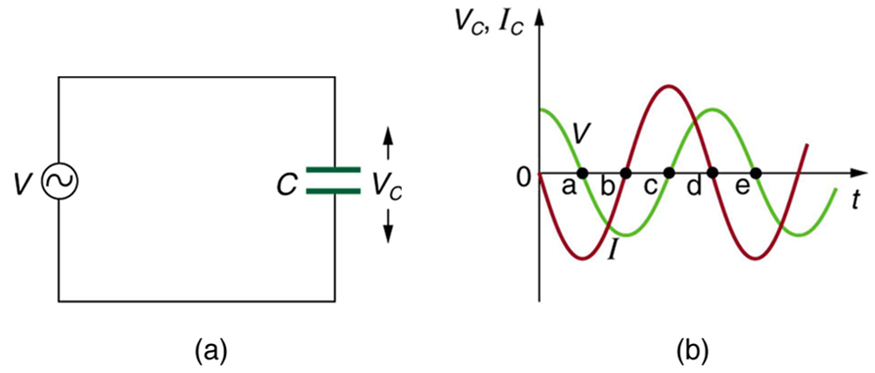
The graph in [link] starts with voltage across the capacitor at a maximum. The current is zero at this point, because the capacitor is fully charged and halts the flow. Then voltage drops and the current becomes negative as the capacitor discharges. At point a, the capacitor has fully discharged ( on it) and the voltage across it is zero. The current remains negative between points a and b, causing the voltage on the capacitor to reverse. This is complete at point b, where the current is zero and the voltage has its most negative value. The current becomes positive after point b, neutralizing the charge on the capacitor and bringing the voltage to zero at point c, which allows the current to reach its maximum. Between points c and d, the current drops to zero as the voltage rises to its peak, and the process starts to repeat. Throughout the cycle, the voltage follows what the current is doing by one-fourth of a cycle:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?