| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plan an experiment to analyze changes to a system's angular momentum. Choose a system capable of rotational motion such as a lazy Susan or a merry-go-round. Predict how the angular momentum of this system will change when you add an object to the lazy Susan or jump onto the merry-go-round. What variables can you control? What are you measuring? In other words, what are your independent and dependent variables? Are there any independent variables that it would be useful to keep constant (angular velocity, perhaps)? Collect data in order to calculate or estimate the angular momentum of your system when in motion. What do you observe? Collect data in order to calculate the change in angular momentum as a result of the interaction you performed.
Using your data, how does the angular momentum vary with the size and location of an object added to the rotating system?
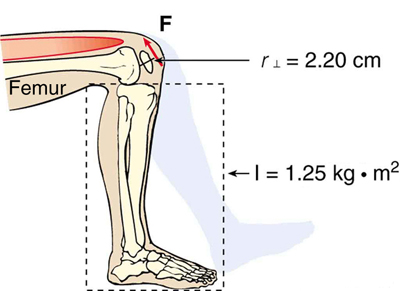
The person whose leg is shown in [link] kicks his leg by exerting a 2000-N force with his upper leg muscle. The effective perpendicular lever arm is 2.20 cm. Given the moment of inertia of the lower leg is , (a) find the angular acceleration of the leg. (b) Neglecting the gravitational force, what is the rotational kinetic energy of the leg after it has rotated through (1.00 rad)?
Strategy
The angular acceleration can be found using the rotational analog to Newton's second law, or . The moment of inertia is given and the torque can be found easily from the given force and perpendicular lever arm. Once the angular acceleration is known, the final angular velocity and rotational kinetic energy can be calculated.
Solution to (a)
From the rotational analog to Newton's second law, the angular acceleration is
Because the force and the perpendicular lever arm are given and the leg is vertical so that its weight does not create a torque, the net torque is thus
Substituting this value for the torque and the given value for the moment of inertia into the expression for gives
Solution to (b)
The final angular velocity can be calculated from the kinematic expression
or
because the initial angular velocity is zero. The kinetic energy of rotation is
so it is most convenient to use the value of just found and the given value for the moment of inertia. The kinetic energy is then
Discussion
These values are reasonable for a person kicking his leg starting from the position shown. The weight of the leg can be neglected in part (a) because it exerts no torque when the center of gravity of the lower leg is directly beneath the pivot in the knee. In part (b), the force exerted by the upper leg is so large that its torque is much greater than that created by the weight of the lower leg as it rotates. The rotational kinetic energy given to the lower leg is enough that it could give a ball a significant velocity by transferring some of this energy in a kick.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?