| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In solving part (a) of the preceding example, the expression we found for is valid for any projectile motion where air resistance is negligible. Call the maximum height ; then,
This equation defines the maximum height of a projectile and depends only on the vertical component of the initial velocity.
It is important to set up a coordinate system when analyzing projectile motion. One part of defining the coordinate system is to define an origin for the and positions. Often, it is convenient to choose the initial position of the object as the origin such that and . It is also important to define the positive and negative directions in the and directions. Typically, we define the positive vertical direction as upwards, and the positive horizontal direction is usually the direction of the object's motion. When this is the case, the vertical acceleration, , takes a negative value (since it is directed downwards towards the Earth). However, it is occasionally useful to define the coordinates differently. For example, if you are analyzing the motion of a ball thrown downwards from the top of a cliff, it may make sense to define the positive direction downwards since the motion of the ball is solely in the downwards direction. If this is the case, takes a positive value.
Kilauea in Hawaii is the world's most continuously active volcano. Very active volcanoes characteristically eject red-hot rocks and lava rather than smoke and ash. Suppose a large rock is ejected from the volcano with a speed of 25.0 m/s and at an angle above the horizontal, as shown in [link] . The rock strikes the side of the volcano at an altitude 20.0 m lower than its starting point. (a) Calculate the time it takes the rock to follow this path. (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the rock's velocity at impact?
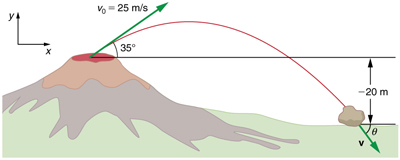
Strategy
Again, resolving this two-dimensional motion into two independent one-dimensional motions will allow us to solve for the desired quantities. The time a projectile is in the air is governed by its vertical motion alone. We will solve for first. While the rock is rising and falling vertically, the horizontal motion continues at a constant velocity. This example asks for the final velocity. Thus, the vertical and horizontal results will be recombined to obtain and at the final time determined in the first part of the example.
Solution for (a)
While the rock is in the air, it rises and then falls to a final position 20.0 m lower than its starting altitude. We can find the time for this by using
If we take the initial position to be zero, then the final position is Now the initial vertical velocity is the vertical component of the initial velocity, found from = ( )( ) = . Substituting known values yields
Rearranging terms gives a quadratic equation in :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?