| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We know that . Substituting this equation into the relationship above gives
Substituting for gives an equation relating the distances measured by different observers.
Length contraction is the shortening of the measured length of an object moving relative to the observer’s frame.
If we measure the length of anything moving relative to our frame, we find its length to be smaller than the proper length that would be measured if the object were stationary. For example, in the muon’s reference frame, the distance between the points where it was produced and where it decayed is shorter. Those points are fixed relative to the Earth but moving relative to the muon. Clouds and other objects are also contracted along the direction of motion in the muon’s reference frame.
One of the consequences of Einstein’s theory of special relativity is the concept of length contraction. Consider a 10-cm stick. If this stick is traveling past you at a speed close to the speed of light, its length will no longer appear to be 10 cm. The length measured when the stick is at rest is calledits proper length. The length measured when the stick is in motion close to the speed of light will always be less than the proper length. This is what is known as length contraction. But the effect of length contraction can only be observed if the stick moves really fast—close to the speed of light. In principle, when the speed of the stick is equal to the speed of light,the stick should have no length.
Suppose an astronaut, such as the twin discussed in Simultaneity and Time Dilation , travels so fast that . (a) She travels from the Earth to the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, 4.300 light years (ly) away as measured by an Earth-bound observer. How far apart are the Earth and Alpha Centauri as measured by the astronaut? (b) In terms of , what is her velocity relative to the Earth? You may neglect the motion of the Earth relative to the Sun. (See [link] .)
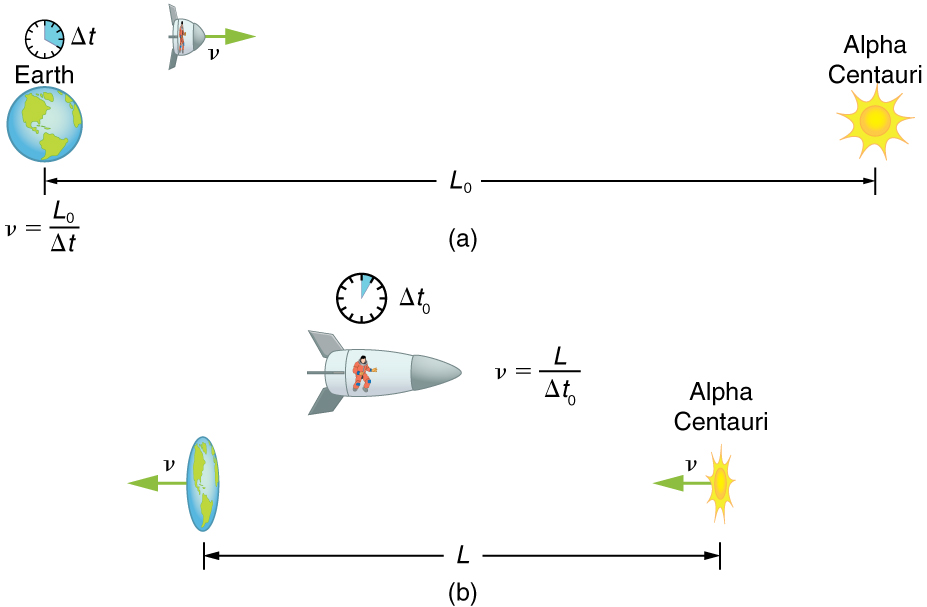
Strategy
First note that a light year (ly) is a convenient unit of distance on an astronomical scale—it is the distance light travels in a year. For part (a), note that the 4.300 ly distance between the Alpha Centauri and the Earth is the proper distance , because it is measured by an Earth-bound observer to whom both stars are (approximately) stationary. To the astronaut, the Earth and the Alpha Centauri are moving by at the same velocity, and so the distance between them is the contracted length . In part (b), we are given , and so we can find by rearranging the definition of to express in terms of .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?