| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Research begun by people such as New Zealander Ernest Rutherford soon after the discovery of nuclear radiation indicated that different types of rays are emitted. Eventually, three types were distinguished and named alpha , beta , and gamma , because, like x-rays, their identities were initially unknown. [link] shows what happens if the rays are passed through a magnetic field. The s are unaffected, while the s and s are deflected in opposite directions, indicating the s are positive, the s negative, and the s uncharged. Rutherford used both magnetic and electric fields to show that s have a positive charge twice the magnitude of an electron, or . In the process, he found the s charge to mass ratio to be several thousand times smaller than the electron’s. Later on, Rutherford collected s from a radioactive source and passed an electric discharge through them, obtaining the spectrum of recently discovered helium gas. Among many important discoveries made by Rutherford and his collaborators was the proof that radiation is the emission of a helium nucleus . Rutherford won the Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1908 for his early work. He continued to make important contributions until his death in 1934.
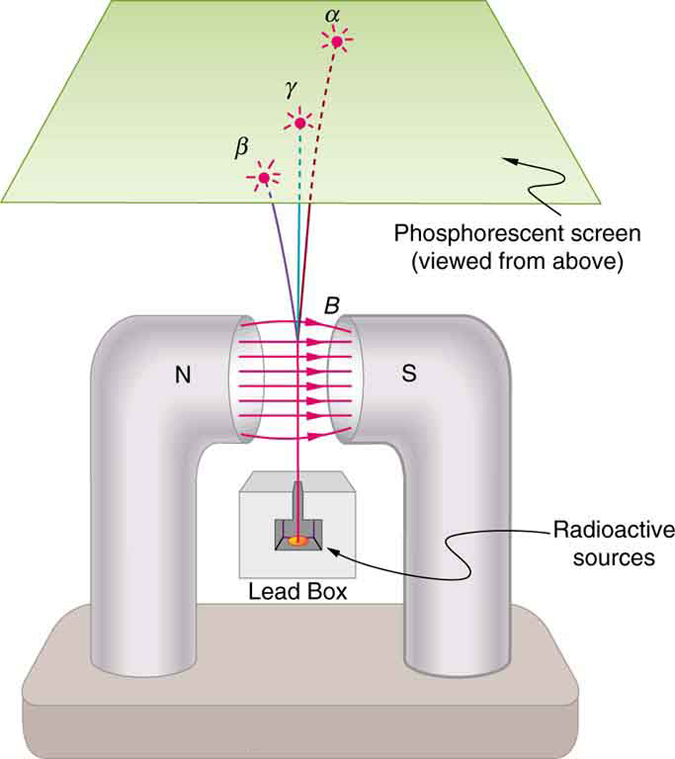
Other researchers had already proved that s are negative and have the same mass and same charge-to-mass ratio as the recently discovered electron. By 1902, it was recognized that radiation is the emission of an electron . Although s are electrons, they do not exist in the nucleus before it decays and are not ejected atomic electrons—the electron is created in the nucleus at the instant of decay.
Since s remain unaffected by electric and magnetic fields, it is natural to think they might be photons. Evidence for this grew, but it was not until 1914 that this was proved by Rutherford and collaborators. By scattering radiation from a crystal and observing interference, they demonstrated that radiation is the emission of a high-energy photon by a nucleus . In fact, radiation comes from the de-excitation of a nucleus, just as an x ray comes from the de-excitation of an atom. The names " ray" and "x ray" identify the source of the radiation. At the same energy, rays and x rays are otherwise identical.
| Type of Radiation | Range |
|---|---|
| -Particles | A sheet of paper, a few cm of air, fractions of a mm of tissue |
| -Particles | A thin aluminum plate, or tens of cm of tissue |
| Rays | Several cm of lead or meters of concrete |
Two of the most important characteristics of , , and rays were recognized very early. All three types of nuclear radiation produce ionization in materials, but they penetrate different distances in materials—that is, they have different ranges . Let us examine why they have these characteristics and what are some of the consequences.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?