| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Two general rules for combining quarks to form hadrons are:
One of the clever things about this scheme is that only integral charges result, even though the quarks have fractional charge.
All quark combinations are possible. [link] lists some of these combinations. When Gell-Mann and Zweig proposed the original three quark flavors, particles corresponding to all combinations of those three had not been observed. The pattern was there, but it was incomplete—much as had been the case in the periodic table of the elements and the chart of nuclides. The particle, in particular, had not been discovered but was predicted by quark theory. Its combination of three strange quarks, , gives it a strangeness of (see [link] ) and other predictable characteristics, such as spin, charge, approximate mass, and lifetime. If the quark picture is complete, the should exist. It was first observed in 1964 at Brookhaven National Laboratory and had the predicted characteristics as seen in [link] . The discovery of the was convincing indirect evidence for the existence of the three original quark flavors and boosted theoretical and experimental efforts to further explore particle physics in terms of quarks.
Patterns in the properties of atoms allowed the periodic table to be developed. From it, previously unknown elements were predicted and observed. Similarly, patterns were observed in the properties of nuclei, leading to the chart of nuclides and successful predictions of previously unknown nuclides. Now with particle physics, patterns imply a quark substructure that, if taken literally, predicts previously unknown particles. These have now been observed in another triumph of underlying unity.
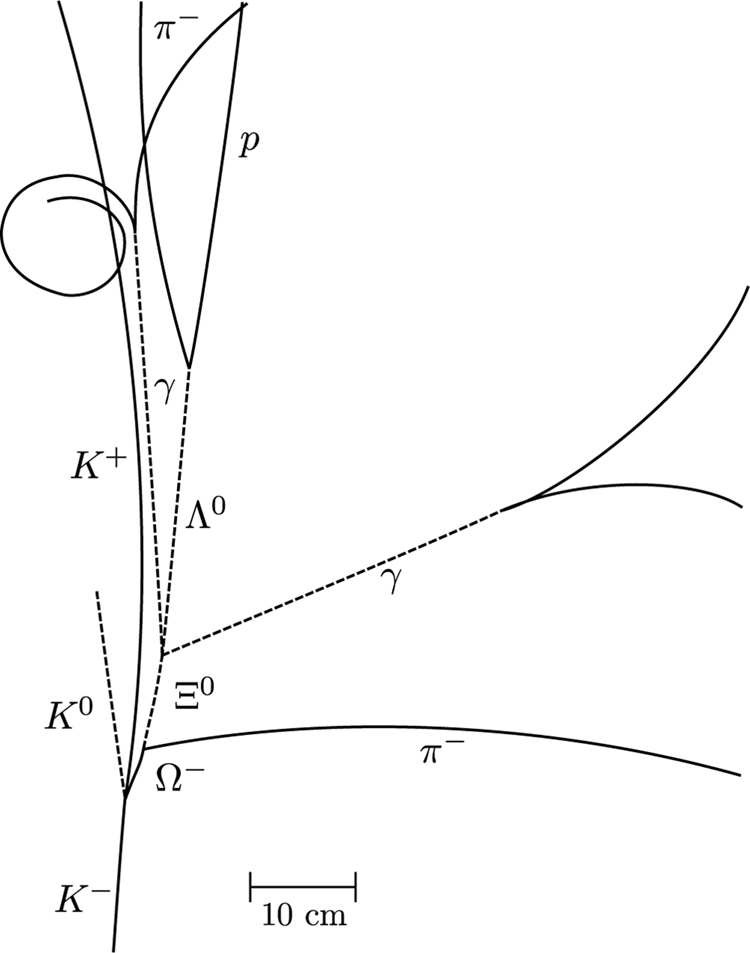
Verify the quantum numbers given for the particle in [link] by adding the quantum numbers for its quark composition as given in [link] .
Strategy
The composition of the is given as in [link] . The quantum numbers for the constituent quarks are given in [link] . We will not consider spin, because that is not given for the . But we can check on charge and the other quantum numbers given for the quarks.
Solution
The total charge of uss is , which is correct for the . The baryon number is , also correct since the is a matter baryon and has , as listed in [link] . Its strangeness is , also as expected from [link] . Its charm, bottomness, and topness are 0, as are its lepton family numbers (it is not a lepton).
Discussion
This procedure is similar to what the inventors of the quark hypothesis did when checking to see if their solution to the puzzle of particle patterns was correct. They also checked to see if all combinations were known, thereby predicting the previously unobserved as the completion of a pattern.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?