| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
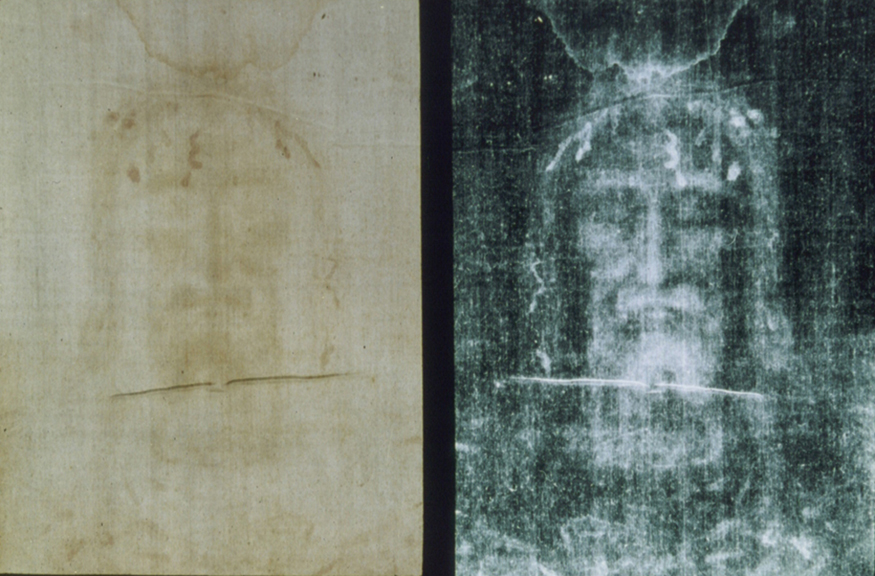
Calculate the age of the Shroud of Turin given that the amount of found in it is 92% of that in living tissue.
Strategy
Knowing that 92% of the remains means that . Therefore, the equation can be used to find . We also know that the half-life of is 5730 y, and so once is known, we can use the equation to find and then find as requested. Here, we postulate that the decrease in is solely due to nuclear decay.
Solution
Solving the equation for gives
Thus,
Taking the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation yields
so that
Rearranging to isolate gives
Now, the equation can be used to find for . Solving for and substituting the known half-life gives
We enter this value into the previous equation to find :
Discussion
This dates the material in the shroud to 1988–690 = a.d. 1300. Our calculation is only accurate to two digits, so that the year is rounded to 1300. The values obtained at the three independent laboratories gave a weighted average date of a.d. . The uncertainty is typical of carbon-14 dating and is due to the small amount of in living tissues, the amount of material available, and experimental uncertainties (reduced by having three independent measurements). It is meaningful that the date of the shroud is consistent with the first record of its existence and inconsistent with the period in which Jesus lived.
There are other forms of radioactive dating. Rocks, for example, can sometimes be dated based on the decay of . The decay series for ends with , so that the ratio of these nuclides in a rock is an indication of how long it has been since the rock solidified. The original composition of the rock, such as the absence of lead, must be known with some confidence. However, as with carbon-14 dating, the technique can be verified by a consistent body of knowledge. Since has a half-life of y, it is useful for dating only very old materials, showing, for example, that the oldest rocks on Earth solidified about years ago.
What do we mean when we say a source is highly radioactive? Generally, this means the number of decays per unit time is very high. We define activity to be the rate of decay expressed in decays per unit time. In equation form, this is
where is the number of decays that occur in time . The SI unit for activity is one decay per second and is given the name becquerel (Bq) in honor of the discoverer of radioactivity. That is,
Activity is often expressed in other units, such as decays per minute or decays per year. One of the most common units for activity is the curie (Ci), defined to be the activity of 1 g of , in honor of Marie Curie’s work with radium. The definition of curie is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?