| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Success in problem solving is obviously necessary to understand and apply physical principles, not to mention the more immediate need of passing exams. The basics of problem solving, presented earlier in this text, are followed here, but specific strategies useful in applying Newton’s laws of motion are emphasized. These techniques also reinforce concepts that are useful in many other areas of physics. Many problem-solving strategies are stated outright in the worked examples, and so the following techniques should reinforce skills you have already begun to develop.
Step 1. As usual, it is first necessary to identify the physical principles involved.
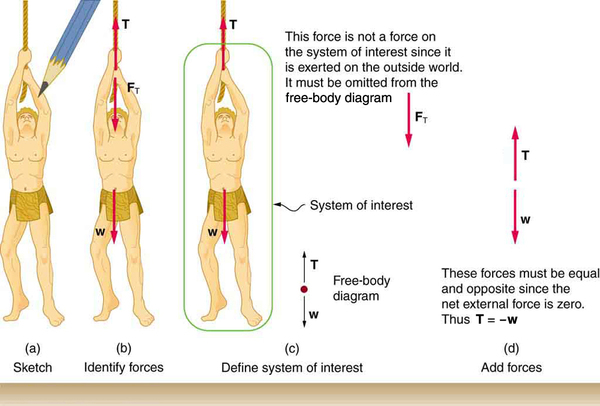
Once it is determined that Newton’s laws of motion are involved (if the problem involves forces), it is particularly important to draw a careful sketch of the situation . Such a sketch is shown in
[link] (a). Then, as in
[link] (b), use arrows to represent all forces, label them carefully, and make their lengths and directions correspond to the forces they represent (whenever sufficient information exists).
Step 2. Identify what needs to be determined and what is known or can be inferred from the problem as stated. That is, make a list of knowns and unknowns.
Then carefully determine the system of interest . This decision is a crucial step, since Newton’s second law involves only external forces. Once the system of interest has been identified, it becomes possible to determine which forces are external and which are internal, a necessary step to employ Newton’s second law. (See
[link] (c).) Newton’s third law may be used to identify whether forces are exerted between components of a system (internal) or between the system and something outside (external). As illustrated earlier in this chapter, the system of interest depends on what question we need to answer. This choice becomes easier with practice, eventually developing into an almost unconscious process. Skill in clearly defining systems will be beneficial in later chapters as well.
A diagram showing the system of interest and all of the external forces is called a
free-body diagram . Only forces are shown on free-body diagrams, not acceleration or velocity. We have drawn several of these in worked examples.
[link] (c) shows a free-body diagram for the system of interest. Note that no internal forces are shown in a free-body diagram.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?