| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Particle physics seems symmetric in matter and antimatter. Why isn’t the cosmos? The answer is that particle physics is not quite perfectly symmetric in this regard. The decay of one of the neutral -mesons, for example, preferentially creates more matter than antimatter. This is caused by a fundamental small asymmetry in the basic forces. This small asymmetry produced slightly more matter than antimatter in the early universe. If there was only one part in more matter (a small asymmetry), the rest would annihilate pair for pair, leaving nearly pure matter to form the stars and galaxies we see today. So the vast number of stars we observe may be only a tiny remnant of the original matter created in the Big Bang. Here at last we see a very real and important asymmetry in nature. Rather than be disturbed by an asymmetry, most physicists are impressed by how small it is. Furthermore, if the universe were completely symmetric, the mutual annihilation would be more complete, leaving far less matter to form us and the universe we know.
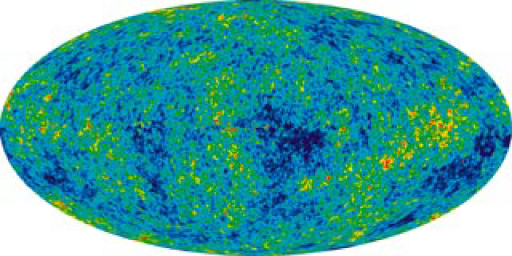
A satellite called the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) carried an instrument that made very sensitive and accurate measurements of the CMBR. In April of 1992, there was extraordinary publicity of COBE’s first results—there were small fluctuations in the CMBR. Further measurements were carried out by experiments including NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), which launched in 2001. Data from WMAP provided a much more detailed picture of the CMBR fluctuations. (See [link] .) These amount to temperature fluctuations of only out of 2.7 K, better than one part in 1000. The WMAP experiment will be followed up by the European Space Agency’s Planck Surveyor, which launched in 2009.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?