| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Particle physics as we know it today began with the ideas of Hideki Yukawa in 1935. Physicists had long been concerned with how forces are transmitted, finding the concept of fields, such as electric and magnetic fields to be very useful. A field surrounds an object and carries the force exerted by the object through space. Yukawa was interested in the strong nuclear force in particular and found an ingenious way to explain its short range. His idea is a blend of particles, forces, relativity, and quantum mechanics that is applicable to all forces. Yukawa proposed that force is transmitted by the exchange of particles (called carrier particles). The field consists of these carrier particles.
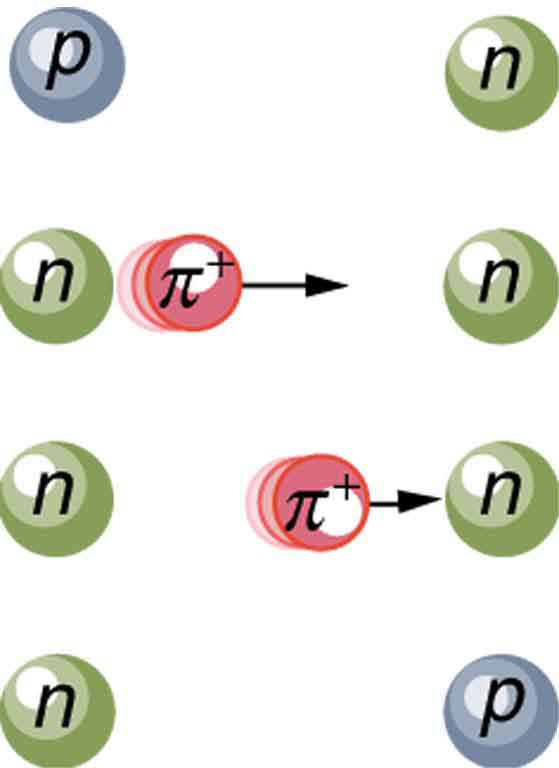
Specifically for the strong nuclear force, Yukawa proposed that a previously unknown particle, now called a pion , is exchanged between nucleons, transmitting the force between them. [link] illustrates how a pion would carry a force between a proton and a neutron. The pion has mass and can only be created by violating the conservation of mass-energy. This is allowed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle if it occurs for a sufficiently short period of time. As discussed in Probability: The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle the Heisenberg uncertainty principle relates the uncertainties in energy and in time by
where is Planck’s constant. Therefore, conservation of mass-energy can be violated by an amount for a time in which time no process can detect the violation. This allows the temporary creation of a particle of mass , where . The larger the mass and the greater the , the shorter is the time it can exist. This means the range of the force is limited, because the particle can only travel a limited distance in a finite amount of time. In fact, the maximum distance is , where c is the speed of light. The pion must then be captured and, thus, cannot be directly observed because that would amount to a permanent violation of mass-energy conservation. Such particles (like the pion above) are called virtual particles , because they cannot be directly observed but their effects can be directly observed. Realizing all this, Yukawa used the information on the range of the strong nuclear force to estimate the mass of the pion, the particle that carries it. The steps of his reasoning are approximately retraced in the following worked example:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?