| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Examining the above table, you can see that as the number of electrons in an atom increases from 1 in hydrogen to 2 in helium and so on, the lowest-energy shell gets filled first—that is, the shell fills first, and then the shell begins to fill. Within a shell, the subshells fill starting with the lowest , or with the subshell, then the , and so on, usually until all subshells are filled. The first exception to this occurs for potassium, where the subshell begins to fill before any electrons go into the subshell. The next exception is not shown in [link] ; it occurs for rubidium, where the subshell starts to fill before the subshell. The reason for these exceptions is that electrons have probability clouds that penetrate closer to the nucleus and, thus, are more tightly bound (lower in energy).
[link] shows the periodic table of the elements, through element 118. Of special interest are elements in the main groups, namely, those in the columns numbered 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18.
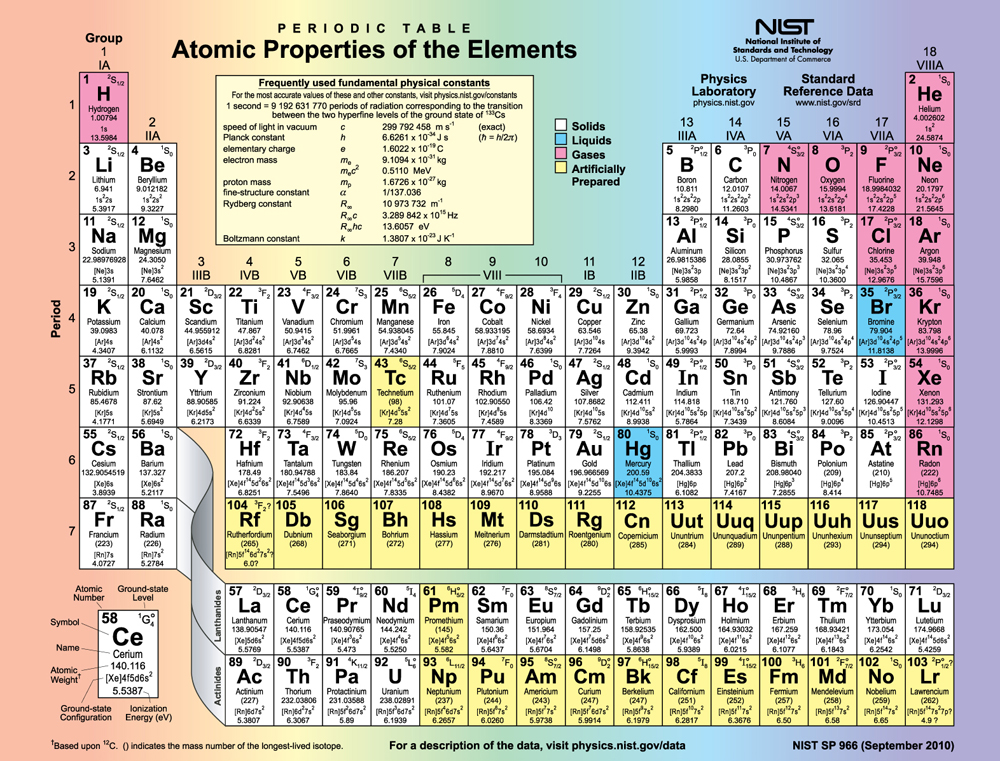
The number of electrons in the outermost subshell determines the atom’s chemical properties, since it is these electrons that are farthest from the nucleus and thus interact most with other atoms. If the outermost subshell can accept or give up an electron easily, then the atom will be highly reactive chemically. Each group in the periodic table is characterized by its outermost electron configuration. Perhaps the most familiar is Group 18 (Group VIII), the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, etc.). These gases are all characterized by a filled outer subshell that is particularly stable. This means that they have large ionization energies and do not readily give up an electron. Furthermore, if they were to accept an extra electron, it would be in a significantly higher level and thus loosely bound. Chemical reactions often involve sharing electrons. Noble gases can be forced into unstable chemical compounds only under high pressure and temperature.
Group 17 (Group VII) contains the halogens, such as fluorine, chlorine, iodine and bromine, each of which has one less electron than a neighboring noble gas. Each halogen has 5 electrons (a configuration), while the subshell can hold 6 electrons. This means the halogens have one vacancy in their outermost subshell. They thus readily accept an extra electron (it becomes tightly bound, closing the shell as in noble gases) and are highly reactive chemically. The halogens are also likely to form singly negative ions, such as , fitting an extra electron into the vacancy in the outer subshell. In contrast, alkali metals, such as sodium and potassium, all have a single electron in their outermost subshell (an configuration) and are members of Group 1 (Group I). These elements easily give up their extra electron and are thus highly reactive chemically. As you might expect, they also tend to form singly positive ions, such as , by losing their loosely bound outermost electron. They are metals (conductors), because the loosely bound outer electron can move freely.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?