| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
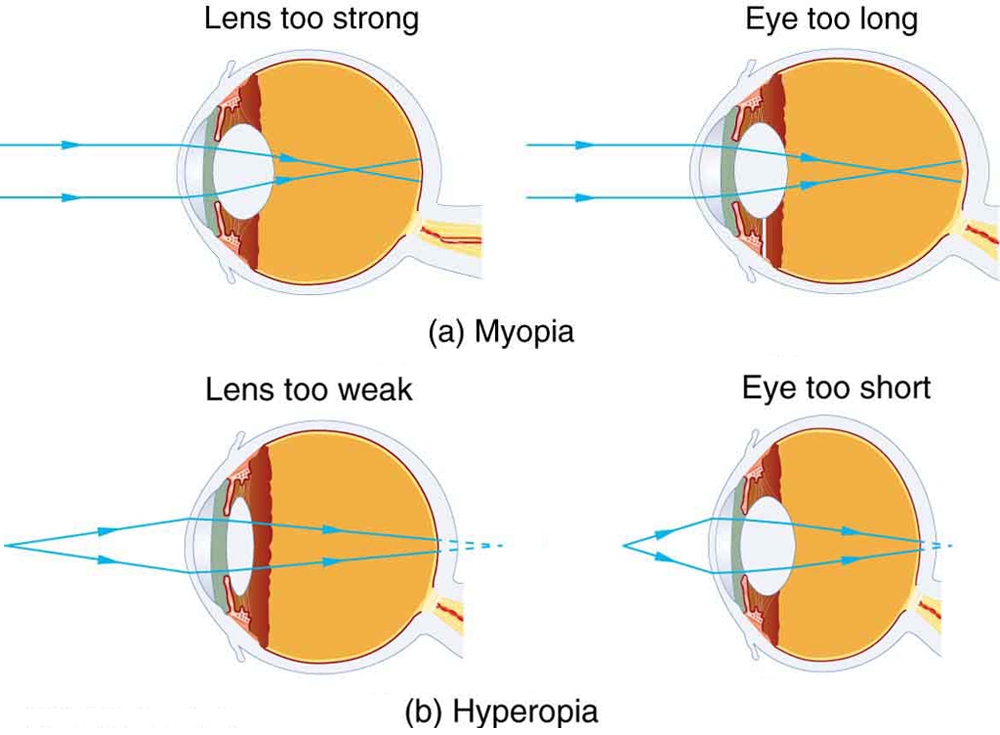
The need for some type of vision correction is very common. Common vision defects are easy to understand, and some are simple to correct. [link] illustrates two common vision defects. Nearsightedness , or myopia , is the inability to see distant objects clearly while close objects are clear. The eye overconverges the nearly parallel rays from a distant object, and the rays cross in front of the retina. More divergent rays from a close object are converged on the retina for a clear image. The distance to the farthest object that can be seen clearly is called the far point of the eye (normally infinity). Farsightedness , or hyperopia , is the inability to see close objects clearly while distant objects may be clear. A farsighted eye does not converge sufficient rays from a close object to make the rays meet on the retina. Less diverging rays from a distant object can be converged for a clear image. The distance to the closest object that can be seen clearly is called the near point of the eye (normally 25 cm).
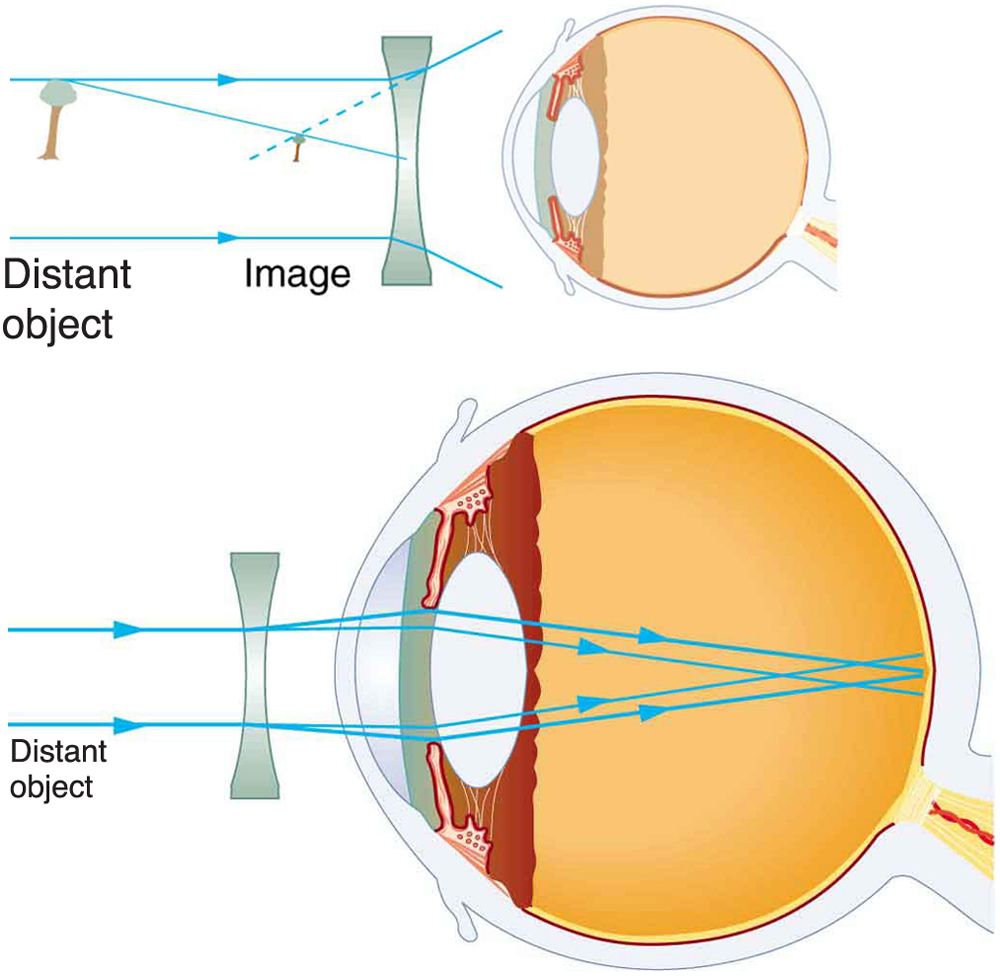
Since the nearsighted eye over converges light rays, the correction for nearsightedness is to place a diverging spectacle lens in front of the eye. This reduces the power of an eye that is too powerful. Another way of thinking about this is that a diverging spectacle lens produces a case 3 image, which is closer to the eye than the object (see [link] ). To determine the spectacle power needed for correction, you must know the person’s far point—that is, you must know the greatest distance at which the person can see clearly. Then the image produced by a spectacle lens must be at this distance or closer for the nearsighted person to be able to see it clearly. It is worth noting that wearing glasses does not change the eye in any way. The eyeglass lens is simply used to create an image of the object at a distance where the nearsighted person can see it clearly. Whereas someone not wearing glasses can see clearly objects that fall between their near point and their far point, someone wearing glasses can see images that fall between their near point and their far point.
What power of spectacle lens is needed to correct the vision of a nearsighted person whose far point is 30.0 cm? Assume the spectacle (corrective) lens is held 1.50 cm away from the eye by eyeglass frames.
Strategy
You want this nearsighted person to be able to see very distant objects clearly. That means the spectacle lens must produce an image 30.0 cm from the eye for an object very far away. An image 30.0 cm from the eye will be 28.5 cm to the left of the spectacle lens (see [link] ). Therefore, we must get when . The image distance is negative, because it is on the same side of the spectacle as the object.
Solution
Since and are known, the power of the spectacle lens can be found using as written earlier:
Since , we obtain:
Discussion
The negative power indicates a diverging (or concave) lens, as expected. The spectacle produces a case 3 image closer to the eye, where the person can see it. If you examine eyeglasses for nearsighted people, you will find the lenses are thinnest in the center. Additionally, if you examine a prescription for eyeglasses for nearsighted people, you will find that the prescribed power is negative and given in units of diopters.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?