| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
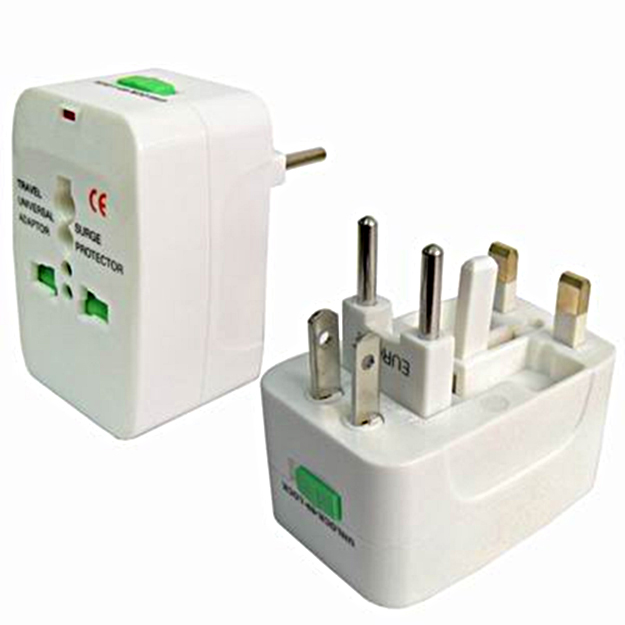
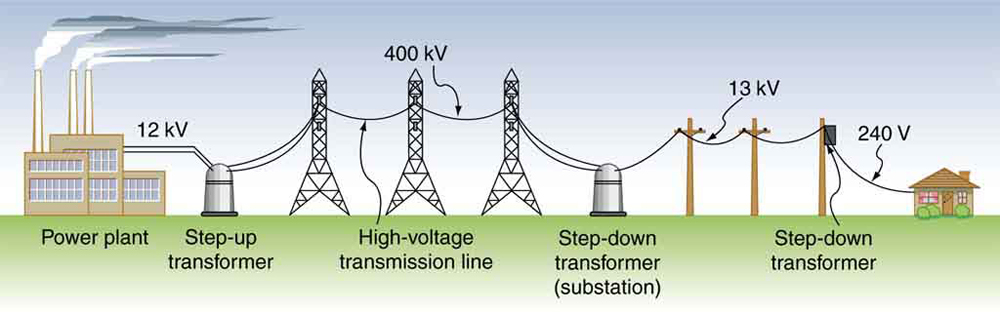
Transformers do what their name implies—they transform voltages from one value to another (The term voltage is used rather than emf, because transformers have internal resistance). For example, many cell phones, laptops, video games, and power tools and small appliances have a transformer built into their plug-in unit (like that in [link] ) that changes 120 V or 240 V AC into whatever voltage the device uses. Transformers are also used at several points in the power distribution systems, such as illustrated in [link] . Power is sent long distances at high voltages, because less current is required for a given amount of power, and this means less line loss, as was discussed previously. But high voltages pose greater hazards, so that transformers are employed to produce lower voltage at the user’s location.

The type of transformer considered in this text—see [link] —is based on Faraday’s law of induction and is very similar in construction to the apparatus Faraday used to demonstrate magnetic fields could cause currents. The two coils are called the primary and secondary coils . In normal use, the input voltage is placed on the primary, and the secondary produces the transformed output voltage. Not only does the iron core trap the magnetic field created by the primary coil, its magnetization increases the field strength. Since the input voltage is AC, a time-varying magnetic flux is sent to the secondary, inducing its AC output voltage.
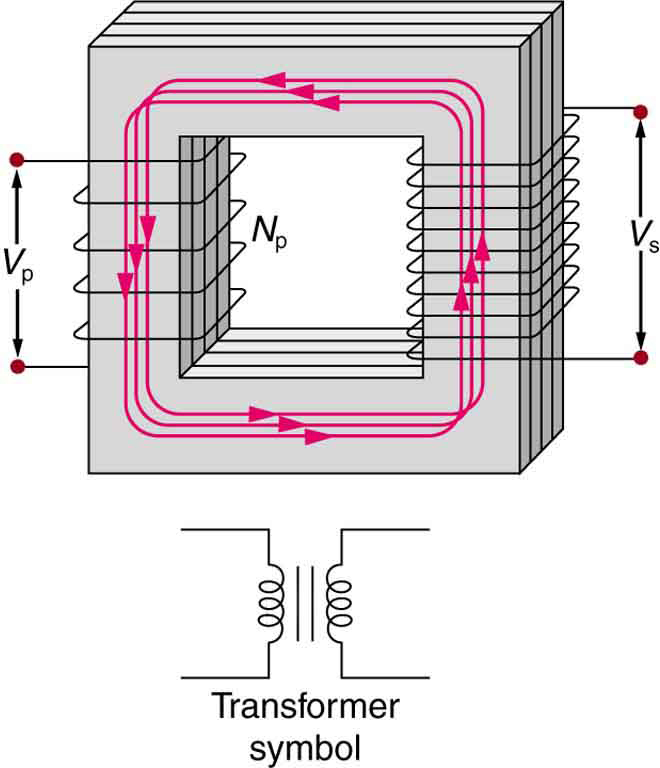
For the simple transformer shown in [link] , the output voltage depends almost entirely on the input voltage and the ratio of the number of loops in the primary and secondary coils. Faraday’s law of induction for the secondary coil gives its induced output voltage to be
where is the number of loops in the secondary coil and / is the rate of change of magnetic flux. Note that the output voltage equals the induced emf ( ), provided coil resistance is small (a reasonable assumption for transformers). The cross-sectional area of the coils is the same on either side, as is the magnetic field strength, and so is the same on either side. The input primary voltage is also related to changing flux by

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?