| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
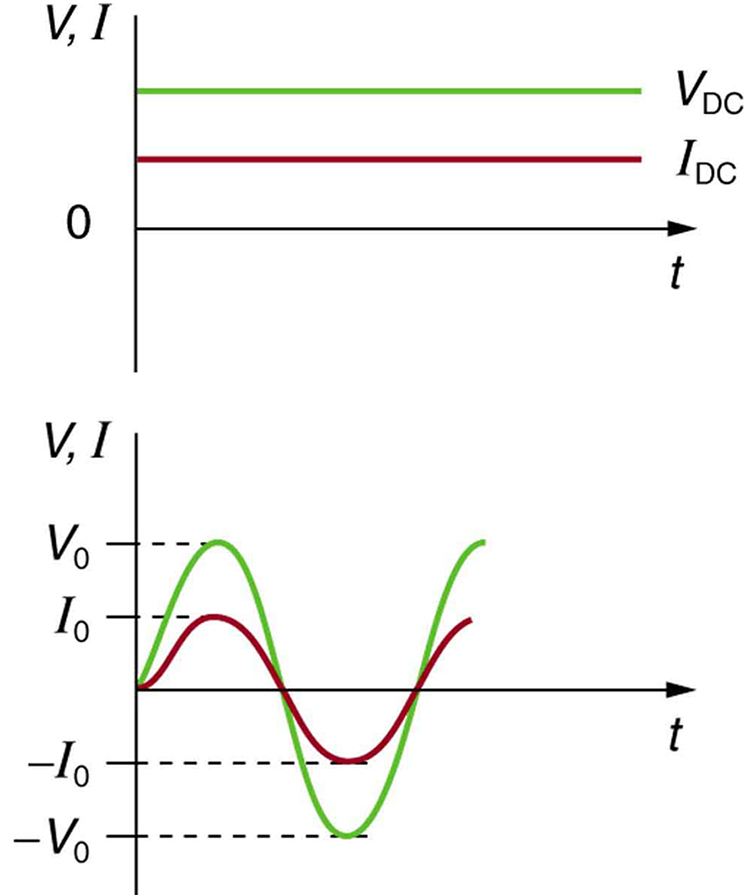
Most of the examples dealt with so far, and particularly those utilizing batteries, have constant voltage sources. Once the current is established, it is thus also a constant. Direct current (DC) is the flow of electric charge in only one direction. It is the steady state of a constant-voltage circuit. Most well-known applications, however, use a time-varying voltage source. Alternating current (AC) is the flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction. If the source varies periodically, particularly sinusoidally, the circuit is known as an alternating current circuit. Examples include the commercial and residential power that serves so many of our needs. [link] shows graphs of voltage and current versus time for typical DC and AC power. The AC voltages and frequencies commonly used in homes and businesses vary around the world.
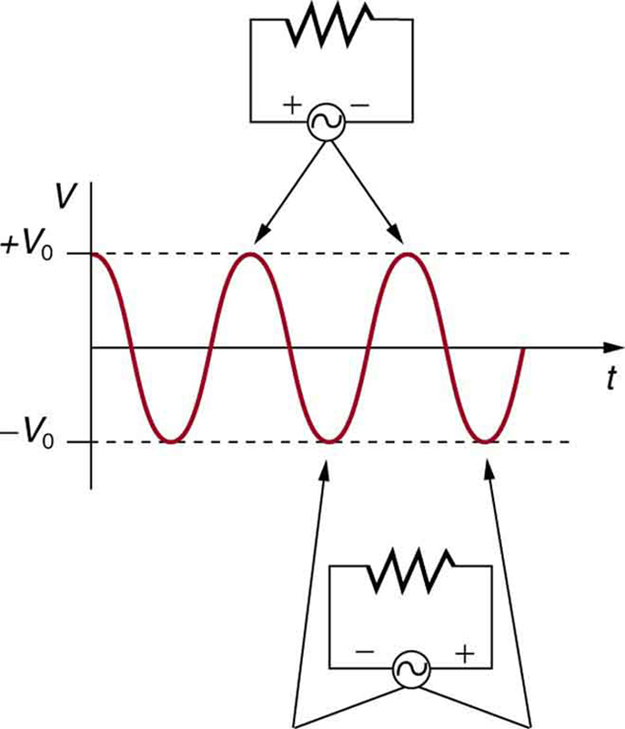
[link] shows a schematic of a simple circuit with an AC voltage source. The voltage between the terminals fluctuates as shown, with the AC voltage given by
where is the voltage at time , is the peak voltage, and is the frequency in hertz. For this simple resistance circuit, , and so the AC current is
where is the current at time , and is the peak current. For this example, the voltage and current are said to be in phase, as seen in [link] (b).
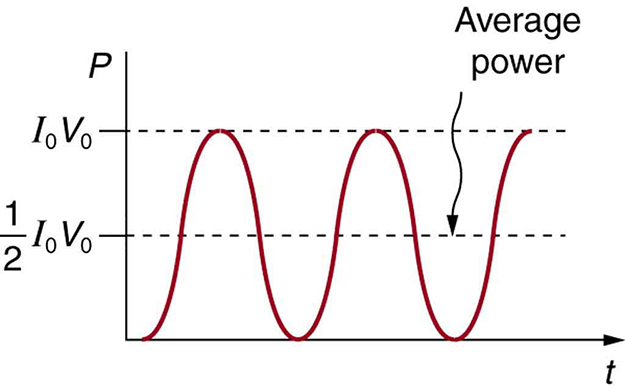
Current in the resistor alternates back and forth just like the driving voltage, since . If the resistor is a fluorescent light bulb, for example, it brightens and dims 120 times per second as the current repeatedly goes through zero. A 120-Hz flicker is too rapid for your eyes to detect, but if you wave your hand back and forth between your face and a fluorescent light, you will see a stroboscopic effect evidencing AC. The fact that the light output fluctuates means that the power is fluctuating. The power supplied is . Using the expressions for and above, we see that the time dependence of power is , as shown in [link] .
Wave your hand back and forth between your face and a fluorescent light bulb. Do you observe the same thing with the headlights on your car? Explain what you observe. Warning: Do not look directly at very bright light .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?