| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Vũ trụ mà ta biết bao gồm vô số các vì sao. Mỗi vì sao là một thiên thể phát sáng, như mặt trời của chúng ta.
Quay quanh mỗi vì sao có các hành tinh, các thiên thạch, sao chổi, theo những quỹ đạo ellip lấy sao làm tiêu điểm, nhờ tương tác của lực hấp dẫn. Quay quanh mỗi hành tinh có các vệ tinh, các vành đai hoặc đám bụi. Mỗi vì sao tạo ra quanh nó một hệ mặt trời, như hệ mặt trời của chúng ta.
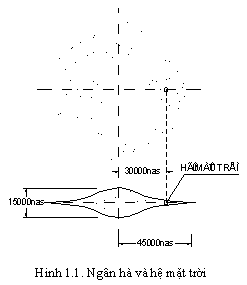
Hàng tỷ hệ mặt trời tụ lại thành một đám, do lực hấp dẫn, tạo ra một thiên hà. Thiên hà của chúng ta được gọi là Ngân hà hay Milky Way, là một trong số hàng tỷ thiên hà trong vũ trụ quan sát được, thiên hà của chúng ta gồm 1011 ngôi sao, có hình đĩa dẹt xoắn ốc, bán kính khoảng = 45.000nas
(nas = năm ánh sáng = 365,25x24x60x60x300.000 =9,5.1012km).
Mỗi hệ mặt trời quay quanh tâm thiên hà với tốc độ hàng trăm km/s. Hệ mặt trời của chúng ta nằm trên rìa ngoài của Ngân hà, cách tâm khoảng 30.000nas, và quay quanh tâm Ngân hà với vận tốc:
vMT= 230km/s.
Vũ trụ mà ta quan sát được hiện nay chứa khoảng 10 tỷ thiên hà, có bán kính 3.1025m, chứa khoảng 1020 ngôi sao với tổng khối lượng khoảng 1050kg.
Để tồn tại dưới tác dụng của lực hấp dẫn, các thiên thể trong vũ trụ phải chuyển động không ngừng. Các hành tinh tự xoay quanh mình và quay quanh mặt trời với tốc độ vài chục km/s, các mặt trời quay quanh tâm thiên hà với tốc độ hàng trăm km/s, các thiên hà quay quanh tâm đại thiên hà với tốc độ hàng nghìn km/s.
Năm 1923, khi sử dụng kính thiên văn vô tuyến ghi phổ bức xạ phát ra từ các thiên hà, Edwin Hubble nhận thấy các vạch quang phổ luôn dịch chuyển về phía bước sóng dài, phía màu đỏ. Hiện tượng dịch về phía đỏ của bức xạ được giải thích bằng hiệu ứng Doppler, là do các thiên thể phát bức xạ đang chuyển động ra xa nơi thu bức xạ, chuyển động rời xa nhau của các thiên hà được phát hiện thấy theo mọi phương, với vận tốc tăng dần theo khoảng cách giữa chúng. Như vậy, các thiên thể trong vũ trụ đang rời xa nhau, và vũ trụ đang dãn nở như quả bóng đang được thổi căng ra.
Dựa vào thực nghiệm, Edwin Hubble mô tả sự dãn nở của vũ trụ bằng định luật sau: Mọi thiên thể trong vũ trụ đang chuyển động ra xa nhau với vận tốc tỷ lệ thuận với khoảng cách r giữa chúng: = -H. , với H 25km/s.106nas là hằng số Hubble.
Thực tế hằng số Hubble chưa thể xác định chính xác, chỉ biết nó nằm trong khoảng (1530)km/s.106nas.
Thực nghiệm cho biết vũ trụ đang dãn nở, các thiên thể đang rời xa nhau. Vậy nếu đi ngược lại thời gian, các thiên thể sẽ tiến lại gần nhau, thể tích vũ trụ sẽ co dần lại. Tại một thời điểm nào đó, toàn bộ vũ trụ sẽ co lại thành một chất điểm, có khối lượng, năng lượng và nhiệt độ vô cùng lớn.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Năng lượng mặt trời- lý thuyết và ứng dụng' conversation and receive update notifications?