| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. Droughts
1.1 The occurrence and cause of droughts
1.1.1 What are droughts?
A drought is a continuous and lengthy period during which there is no or insufficient precipitation. Thus it is associated with a lack of water, but it does not always lead to a disaster. It is the relationship between the community and their environment that will determine whether a drought will develop into a disaster or not. Isolated droughts rarely occur out of the blue. They usually creep up on a community over several years.
1.1.2 Where do droughts occur?
Study figure 1. It is a world map showing the areas where most droughts occur. You will note that certain countries experience more droughts than others, but that the African continent and India suffer the most from serious droughts.

Figure 1
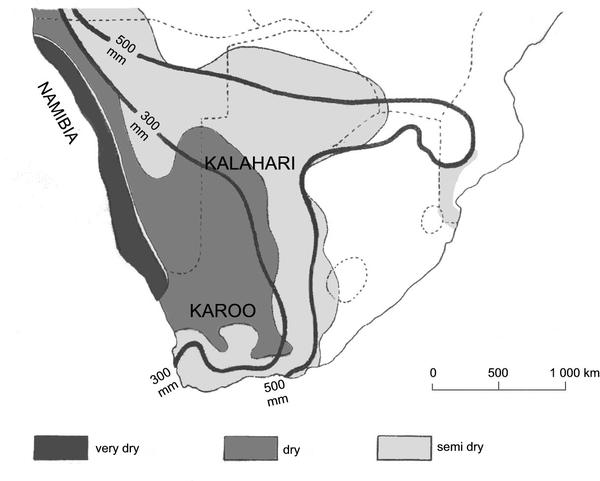
Figure 2
a) Make an estimation as to what percentage of South Africa experiences rainfall of less than 500 mm per year.
b) Where in South Africa are droughts most likely to occur? Why?
c) Where in South Africa are droughts least likely to occur? Why?
d) Name ways in which a farmer in the Northern Cape can take precautionary steps against future droughts.
1.1.3 What causes droughts?
Water is essential for life on earth. A drought is the result of a lack of water. Many people think that a drought occurs merely because it doesn’t rain. A decrease in rainfall does indeed cause droughts, but this is not the only cause.
Study table 1, which shows how other factors can lead to the disastrous conditions which are associated with droughts.
Table 1:
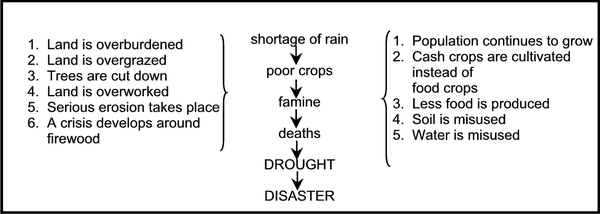
Thus changes in climate are indeed implicated in droughts, but poor environmental management has a greater influence on the disastrous impact of a drought.
1.2 The effect (consequences) of droughts on the lives of people and their socio-economic activities
During a period of about 10 years approximately 60 million people worldwide are affected by droughts, and this number continues to increase. In the 1990s, in Africa alone, 35 million people were affected by drought. What will the situation be in the future?
Study the following list of consequences of droughts:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?