This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses ratios and rates. By the end of the module students should be able to distinguish between denominate and pure numbers and between ratios and rates.
Section overview
- Denominate Numbers and Pure Numbers
- Ratios and Rates
Denominate numbers and pure numbers
Denominate numbers, like and unlike denominate numbers
It is often necessary or convenient to compare two quantities
. Denominate numbers are numbers together with some specified unit. If the units being compared are alike, the denominate numbers are called
like denominate numbers . If units are not alike, the numbers are called
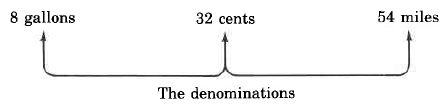
unlike denominate numbers . Examples of denominate numbers are shown in the diagram:
Pure numbers
Numbers that exist purely as numbers and do
not represent amounts of quantities are called
pure numbers . Examples of pure numbers are 8, 254, 0,
,
, and 0.07.
Numbers can be
compared in two ways: subtraction and division.
Comparing numbers by subtraction and division
Comparison of two numbers by subtraction indicates how
much more one number is than another.
Comparison by division indicates how
many times larger or smaller one number is than another.
Comparing pure or like denominate numbers by subtraction
Numbers can be compared by subtraction if and only if they both are like denominate numbers or both pure numbers.
Sample set a
Compare 8 miles and 3 miles by subtraction.
This means that 8 miles is 5 miles more than 3 miles.
Examples of use : I can now jog 8 miles whereas I used to jog only 3 miles. So, I can now jog 5 miles more than I used to.
Compare 12 and 5 by subtraction.
This means that 12 is 7 more than 5.
Comparing 8 miles and 5 gallons by subtraction makes no sense.
Compare 36 and 4 by division.
This means that 36 is 9 times as large as 4. Recall that
can be expressed as
.
Compare 8 miles and 2 miles by division.
This means that 8 miles is 4 times as large as 2 miles.
Example of use : I can jog 8 miles to your 2 miles. Or, for every 2 miles that you jog, I jog 8. So, I jog 4 times as many miles as you jog.
Notice that when like quantities are being compared by division, we drop the units. Another way of looking at this is that the units divide out (cancel).
Compare 30 miles and 2 gallons by division.
Example of use : A particular car goes 30 miles on 2 gallons of gasoline. This is the same as getting 15 miles to 1 gallon of gasoline.
Notice that when the quantities being compared by division are unlike quantities, we do not drop the units.
Practice set a
Make the following comparisons and interpret each one.
Compare 10 diskettes to 2 diskettes by
- subtraction:
- division:
- 8 diskettes; 10 diskettes is 8 diskettes more than 2 diskettes.
- 5; 10 diskettes is 5 times as many diskettes as 2 diskettes.
Compare, if possible, 16 bananas and 2 bags by
- subtraction:
- division:
- Comparison by subtraction makes no sense.
-
, 8 bananas per bag.

