| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Huffman coding deploys variable length coding and then allocates the longer codewords to less frequently occurring symbols and shorter codewords to more regularly occurring symbols. By using this technique it can minimize the overall transmission rate as the regularly occurring symbols are allocated the shorter codewords.
| Symbol | Probability |
| A | 0.10 |
| B | 0.18 |
| C | 0.40 |
| D | 0.05 |
| E | 0.06 |
| F | 0.10 |
| G | 0.07 |
| H | 0.04 |
We have to start with knowledge of the probabilities of occurrence of all the symbols in the alphabet. The table above shows an example of an 8-symbol alphabet, A…H, with the associated probabilities for each of the eight individual symbols.

[link] shows that the entropy of this source data is 2.5524 bits/symbol.
| Symbol | Code |
| A | 000 |
| B | 001 |
| C | 010 |
| D | 011 |
| E | 100 |
| F | 101 |
| G | 110 |
| H | 111 |
This shows the application of very simple coding where, as there are 8 symbols, we adopt a 3-bit code. [link] shows that the entropy of such a source is 2.5524 bit/symbol and, with the fixed 3 bit/symbol length allocated codewords, the efficiency of this simple coder would be only 2.5524/3.0 = 85.08%, which is a rather poor result.
This is a variable length coding technique which involves two processes, reduction and splitting.
We start by listing the symbols in descending order of probability, with the most probable symbol, C, at the top and the least probable symbol, H, at the foot, see left hand side of [link] . Next we reduce the two least probable symbols into a single symbol which has the combined probability of these two symbols summed together. Thus symbols H and D are combined into a single (i.e. reduced) symbol with probability 0.04 + 0.05 = 0.09.
Now the symbols have to be reordered again in descending order of probability. As the probability of the new H+D combined symbol (0.09) is no longer the smallest value it then moves up the reordered list as shown in the second left column in [link] .
This process is progressively repeated as shown in [link] until all symbols are combined into a single symbol whose probability must equal 1.00.
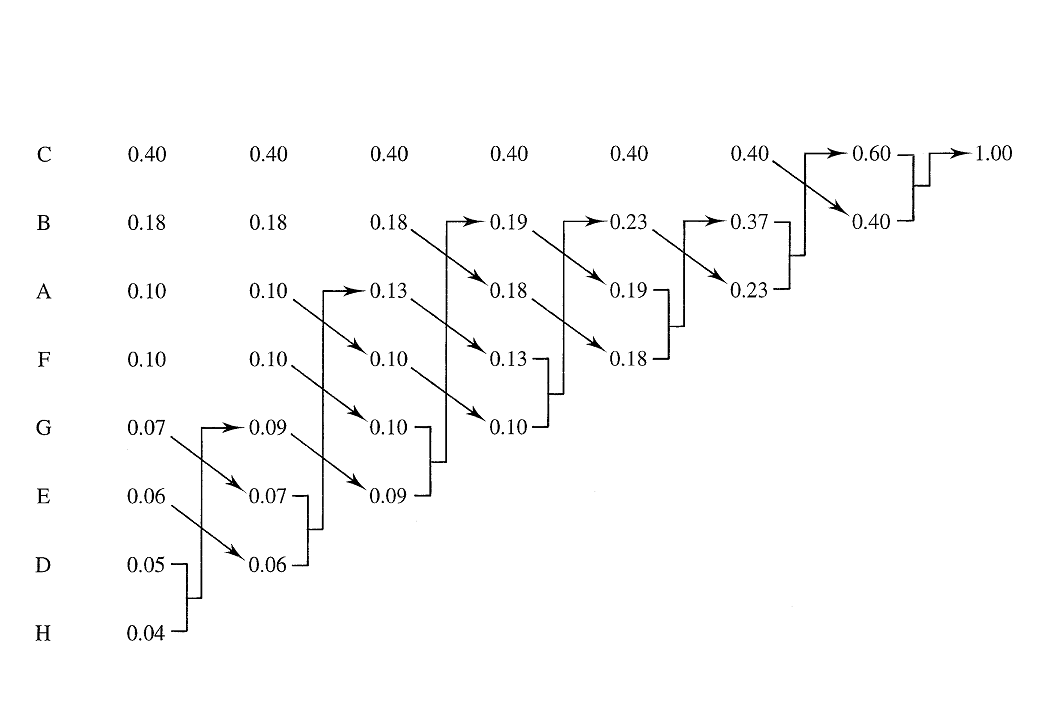
The variable length codewords for each transmitted symbol are now derived by working backwards (from the right) through the tree structure created in [link] , by assigning a 0 to the upper branch of each combining operation and a 1 to the lower branch.
The final “combined symbol” of probability 1.00 is thus split into two parts of probability 0.60 with assigned digit of 0 and another part with probability 0.40 with assigned digit of 1. This latter part with probability 0.40 and assigned digit of 1 actually represents symbol C, [link] .
The “combined symbol” with probability 0.60 (and allocated first digit of 0) is now split into two further parts with probability 0.37 with an additional or second assigned digit of 0 (i.e. its code is now 00) and another part with the remaining probability 0.23 where the additional assigned digit is 1 and associated code will now be 01.

This process is repeated by adding each new digit after the splitting operation to the right of the previous one. Note how this allocates short codes to the more probable symbols and longer codes to the less probable symbols, which are transmitted less often.
| Symbol | Code |
| A | 011 |
| B | 001 |
| C | 1 |
| D | 00010 |
| E | 0101 |
| F | 0000 |
| G | 0100 |
| H | 00011 |
[link] summarises the codewords now allocated to each of the transmitted symbols A…H and also calculates the average length of this source coder as 2.61 bits/symbol. Note the considerable reduction from the fixed length of 3 in the simple 3-bit coder in earlier table.

Now recall from [link] that the entropy of the source data was 2.5524 bits/symbol and the simple fixed length 3-bit code in the earlier table, with a length of 3.00 which gave an efficiency of only 85.08%.
The efficiency of the Huffman coded data with its variable length codewords is therefore 2.5524/2.62 = 97.7% which is a much more acceptable result.
If the symbol probabilities all have values 1/( ) which are integer powers of 2 then Huffmann coding will result in 100% efficiency.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Communications source and channel coding with examples' conversation and receive update notifications?