| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Ships from Europe have sailed round the southern tip of Africa since before 1500 – do you remember Diaz and Da Gama?
In 1652 people from the Netherlands under the leadership of Jan van Riebeeck founded a victualling station at the Cape. Dutch sailing ships had large sails that could make excellent use of wind for sailing.
Much development has taken place since that time. Nowadays most large ships are moved by means of powerful engines.
| Steamship ………………………………Fishing boat …………………………….Passenger ship ……………………….Cargo boat ……………………………. | Tugboat ………………………………….Yacht …………………………………….Oil tanker………………………………… |

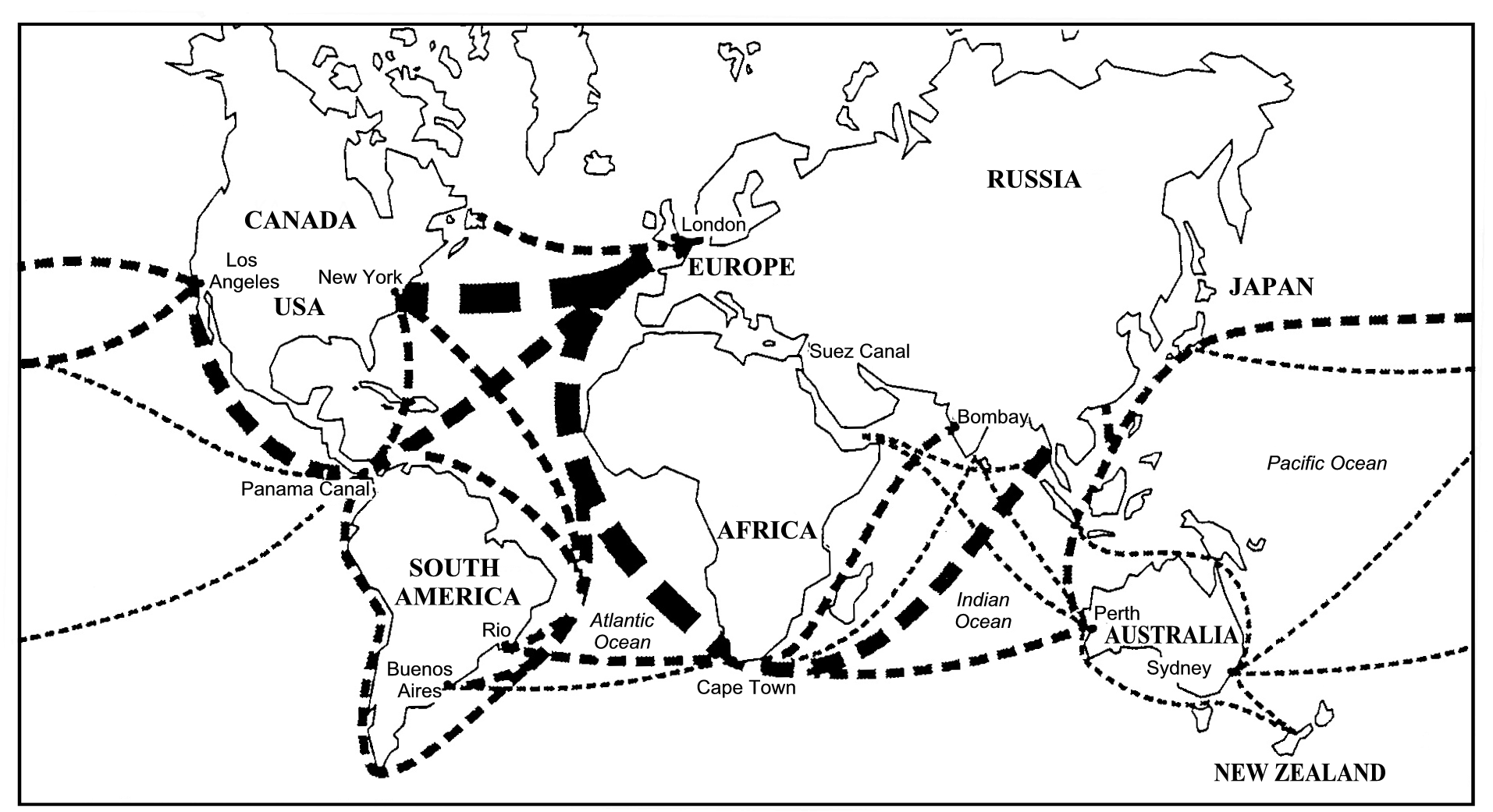
Ocean routes of the world(The thickness of any line corresponds to the tonnage that is transported.)
Refer to an atlas and ask your educator to help you trace Thor Heyerdahl's voyages.
Write a letter to a friend telling him or her about the adventures of any other famous pioneer – male or female – that navigated the seas. What can you learn from this person?
The Norwegian scientist and adventurer Thor Heyerdahl was born in Larvik, Norway, on 6 October 1914. He became famous because he undertook a successful sea voyage on a raft, the Kon-Tiki, which made of balsa wood. (This is a strong but very light kind of wood.) He and his five crewmembers undertook this voyage in 1947 and crossed the Atlantic Ocean from Peru to Polynesia in 97 days. The Polynesian islands are approximately 2 000 km from Peru and lie to the north of New Zeeland. The raft was built like those of the ancient Incas and was named after the Polynesian god Tiki . Heyerdahl wanted to prove that the original inhabitants of Polynesia had come from Peru in South America – not from Asia. He believed that they had been able to undertake such long sea voyages.
The course of his successful voyage was described in his book Kon-Tiki , of which more than 20 million copies have been sold. A film that was made in 1950 and which tells the story of this epic adventure later won an Oscar!

Heyerdahl gained public attention again on 17 May 1970 when he and a crew of seven completed a voyage across the Atlantic Ocean in a 12-metre long boat made of papyrus. This boat was called Ra-2 and was built by Indians from the vicinity of Lake Titicaca in South America where this type of boat is used.
Thor Heyerdahl wanted to prove that the ancient Egyptians had reached the Americas long before Columbus, and that they therefore had had a considerable influence on the American Indian civilization. Heyerdahl's voyage from Morocco in North Africa to Barbados, an island in the Caribbean Sea (960 km away) took about 57 days. Historians did not regard this voyage as important. But Heyerdahl and his crew made use of the opportunity to take samples of seawater to provide proof of the degree of oil pollution that was present in the Atlantic Ocean.
Thor Heyerdahl built a reed boat, the Tigris , with the help of South American Indians from the Lake Titicaca region and completed the distance sailed in the Ra-2 in both directions from 1977 to 1978. The evidence that he gathered of the increase in the oil pollution of the ocean was so shocking to him that he burnt his boat in protest.
During the 1980s, Thor Heyerdahl became more and more involved with campaigns against pollution.

LEARNING OUTCOME 2: HISTORICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING The learner will be able to demonstrate historical knowledge and understanding.
We know this when the learner:
c) Centrally situated for different sea-routes – especially for trade.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 4' conversation and receive update notifications?