| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Consider a situation where the United States and Mexico each have 40 workers. For example, as [link] shows, if the United States divides its labor so that 40 workers are making shoes, then, since it takes four workers in the United States to make 1,000 shoes, a total of 10,000 shoes will be produced. (If four workers can make 1,000 shoes, then 40 workers will make 10,000 shoes). If the 40 workers in the United States are making refrigerators, and each worker can produce 1,000 refrigerators, then a total of 40,000 refrigerators will be produced.
| Country | Shoe Production — using 40 workers | Refrigerator Production — using 40 workers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 10,000 shoes | or | 40,000 refrigerators |
| Mexico | 8,000 shoes | or | 10,000 refrigerators |
As always, the slope of the production possibility frontier for each country is the opportunity cost of one refrigerator in terms of foregone shoe production–when labor is transferred from producing the latter to producing the former (see [link] ).
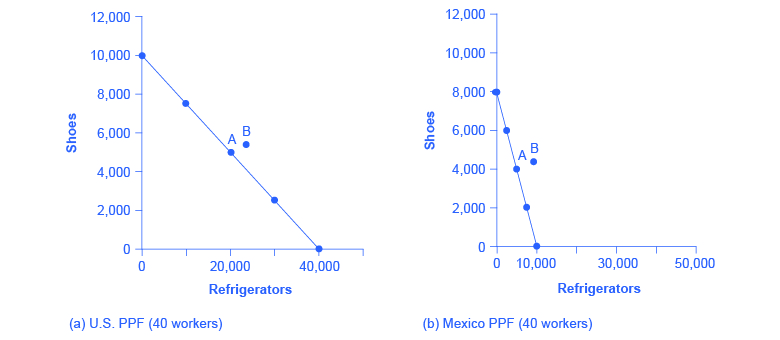
Let’s say that, in the situation before trade, each nation prefers to produce a combination of shoes and refrigerators that is shown at point A. [link] shows the output of each good for each country and the total output for the two countries.
| Country | Current Shoe Production | Current Refrigerator Production |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 5,000 | 20,000 |
| Mexico | 4,000 | 5,000 |
| Total | 9,000 | 25,000 |
Continuing with this scenario, each country transfers some amount of labor toward its area of comparative advantage. For example, the United States transfers six workers away from shoes and toward producing refrigerators. As a result, U.S. production of shoes decreases by 1,500 units (6/4 × 1,000), while its production of refrigerators increases by 6,000 (that is, 6/1 × 1,000). Mexico also moves production toward its area of comparative advantage, transferring 10 workers away from refrigerators and toward production of shoes. As a result, production of refrigerators in Mexico falls by 2,500 (10/4 × 1,000), but production of shoes increases by 2,000 pairs (10/5 × 1,000). Notice that when both countries shift production toward each of their comparative advantages (what they are relatively better at), their combined production of both goods rises, as shown in [link] . The reduction of shoe production by 1,500 pairs in the United States is more than offset by the gain of 2,000 pairs of shoes in Mexico, while the reduction of 2,500 refrigerators in Mexico is more than offset by the additional 6,000 refrigerators produced in the United States.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Openstax microeconomics in ten weeks' conversation and receive update notifications?