| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Once a ligand binds to a receptor, the signal is transmitted through the membrane and into the cytoplasm. Continuation of a signal in this manner is called signal transduction . Signal transduction only occurs with cell-surface receptors because internal receptors are able to interact directly with DNA in the nucleus to initiate protein synthesis.
When a ligand binds to its receptor, conformational changes occur that affect the receptor’s intracellular domain. Conformational changes of the extracellular domain upon ligand binding can propagate through the membrane region of the receptor and lead to activation of the intracellular domain or its associated proteins. In some cases, binding of the ligand causes dimerization of the receptor, which means that two receptors bind to each other to form a stable complex called a dimer. A dimer is a chemical compound formed when two molecules (often identical) join together. The binding of the receptors in this manner enables their intracellular domains to come into close contact and activate each other.
After the ligand binds to the cell-surface receptor, the activation of the receptor’s intracellular components sets off a chain of events that is called a signaling pathway or a signaling cascade. In a signaling pathway, second messengers, enzymes, and activated proteins interact with specific proteins, which are in turn activated in a chain reaction that eventually leads to a change in the cell’s environment ( [link] ). The events in the cascade occur in a series, much like a current flows in a river. Interactions that occur before a certain point are defined as upstream events, and events after that point are called downstream events.
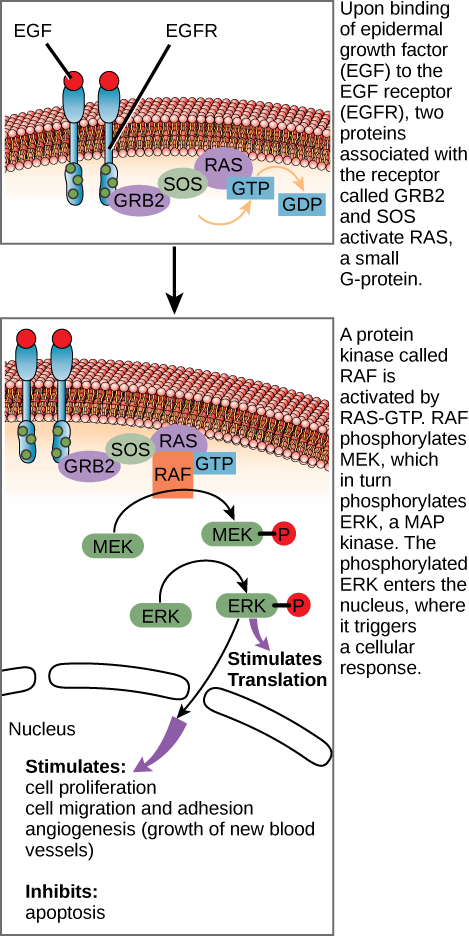
In certain cancers, the GTPase activity of the RAS G-protein is inhibited. This means that the RAS protein can no longer hydrolyze GTP into GDP. What effect would this have on downstream cellular events?
Signaling pathways can get very complicated very quickly because most cellular proteins can affect different downstream events, depending on the conditions within the cell. A single pathway can branch off toward different endpoints based on the interplay between two or more signaling pathways, and the same ligands are often used to initiate different signals in different cell types. This variation in response is due to differences in protein expression in different cell types. Another complicating element is signal integration of the pathways, in which signals from two or more different cell-surface receptors merge to activate the same response in the cell. This process can ensure that multiple external requirements are met before a cell commits to a specific response.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ap biology - part 1: the cell' conversation and receive update notifications?