| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
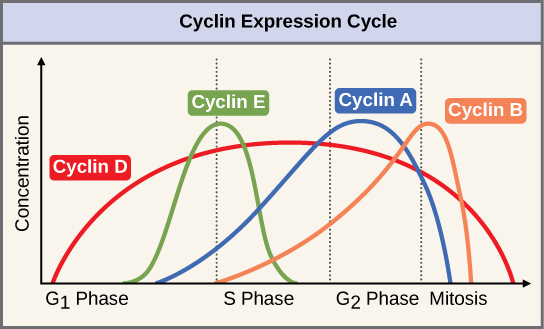
Cyclins regulate the cell cycle only when they are tightly bound to Cdks. To be fully active, the Cdk/cyclin complex must also be phosphorylated in specific locations. Like all kinases, Cdks are enzymes (kinases) that phosphorylate other proteins. Phosphorylation activates the protein by changing its shape. The proteins phosphorylated by Cdks are involved in advancing the cell to the next phase. ( [link] ). The levels of Cdk proteins are relatively stable throughout the cell cycle; however, the concentrations of cyclin fluctuate and determine when Cdk/cyclin complexes form. The different cyclins and Cdks bind at specific points in the cell cycle and thus regulate different checkpoints.
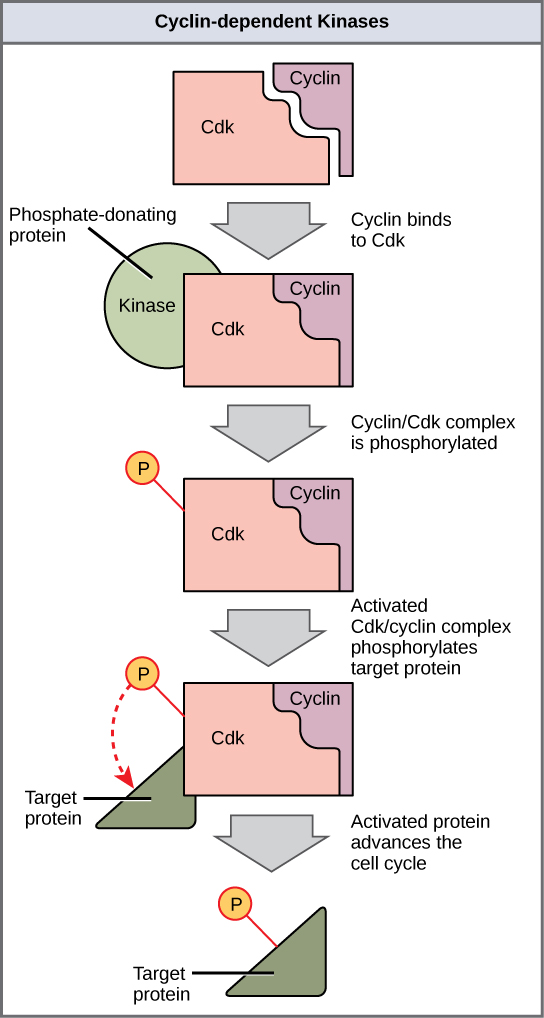
Since the cyclic fluctuations of cyclin levels are based on the timing of the cell cycle and not on specific events, regulation of the cell cycle usually occurs by either the Cdk molecules alone or the Cdk/cyclin complexes. Without a specific concentration of fully activated cyclin/Cdk complexes, the cell cycle cannot proceed through the checkpoints.
Although the cyclins are the main regulatory molecules that determine the forward momentum of the cell cycle, there are several other mechanisms that fine-tune the progress of the cycle with negative, rather than positive, effects. These mechanisms essentially block the progression of the cell cycle until problematic conditions are resolved. Molecules that prevent the full activation of Cdks are called Cdk inhibitors. Many of these inhibitor molecules directly or indirectly monitor a particular cell cycle event. The block placed on Cdks by inhibitor molecules will not be removed until the specific event that the inhibitor monitors is completed.
The second group of cell cycle regulatory molecules are negative regulators. Negative regulators halt the cell cycle. Remember that in positive regulation, active molecules cause the cycle to progress.
The best understood negative regulatory molecules are retinoblastoma protein (Rb) , p53 , and p21 . Retinoblastoma proteins are a group of tumor-suppressor proteins common in many cells. The 53 and 21 designations refer to the functional molecular masses of the proteins (p) in kilodaltons. Much of what is known about cell cycle regulation comes from research conducted with cells that have lost regulatory control. All three of these regulatory proteins were discovered to be damaged or non-functional in cells that had begun to replicate uncontrollably (became cancerous). In each case, the main cause of the unchecked progress through the cell cycle was a faulty copy of the regulatory protein.
Rb, p53, and p21 act primarily at the G 1 checkpoint. p53 is a multi-functional protein that has a major impact on the commitment of a cell to division because it acts when there is damaged DNA in cells that are undergoing the preparatory processes during G 1 . If damaged DNA is detected, p53 halts the cell cycle and recruits enzymes to repair the DNA. If the DNA cannot be repaired, p53 can trigger apoptosis, or cell suicide, to prevent the duplication of damaged chromosomes. As p53 levels rise, the production of p21 is triggered. p21 enforces the halt in the cycle dictated by p53 by binding to and inhibiting the activity of the Cdk/cyclin complexes. As a cell is exposed to more stress, higher levels of p53 and p21 accumulate, making it less likely that the cell will move into the S phase.
Rb exerts its regulatory influence on other positive regulator proteins. Chiefly, Rb monitors cell size. In the active, dephosphorylated state, Rb binds to proteins called transcription factors, most commonly, E2F ( [link] ). Transcription factors “turn on” specific genes, allowing the production of proteins encoded by that gene. When Rb is bound to E2F, production of proteins necessary for the G 1 /S transition is blocked. As the cell increases in size, Rb is slowly phosphorylated until it becomes inactivated. Rb releases E2F, which can now turn on the gene that produces the transition protein, and this particular block is removed. For the cell to move past each of the checkpoints, all positive regulators must be “turned on,” and all negative regulators must be “turned off.”
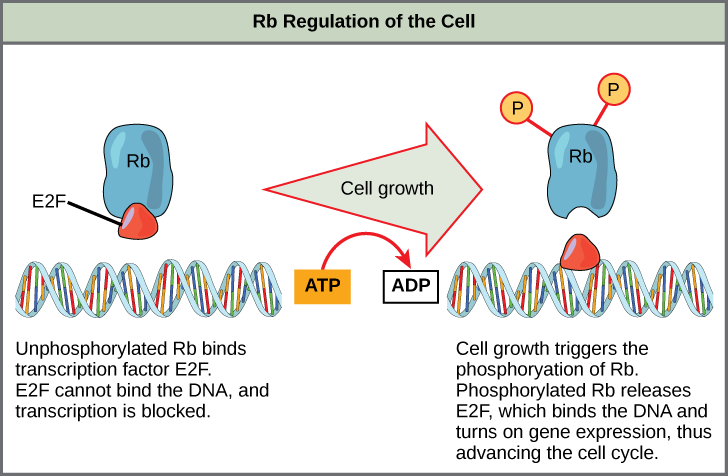
Rb and other proteins that negatively regulate the cell cycle are sometimes called tumor suppressors. Why do you think the name tumor suppressor might be appropriate for these proteins?
Each step of the cell cycle is monitored by internal controls called checkpoints. There are three major checkpoints in the cell cycle: one near the end of G 1 , a second at the G 2 /M transition, and the third during metaphase. Positive regulator molecules allow the cell cycle to advance to the next stage. Negative regulator molecules monitor cellular conditions and can halt the cycle until specific requirements are met.
[link] Rb and other proteins that negatively regulate the cell cycle are sometimes called tumor suppressors. Why do you think the name tumor suppressor might be an appropriate for these proteins?
[link] Rb and other negative regulatory proteins control cell division and therefore prevent the formation of tumors. Mutations that prevent these proteins from carrying out their function can result in cancer.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cell biology' conversation and receive update notifications?