| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The first condition necessary to achieve equilibrium is the one already mentioned: the net external force on the system must be zero. Expressed as an equation, this is simply
Note that if net is zero, then the net external force in any direction is zero. For example, the net external forces along the typical x - and y -axes are zero. This is written as
[link] and [link] illustrate situations where for both static equilibrium (motionless), and dynamic equilibrium (constant velocity).
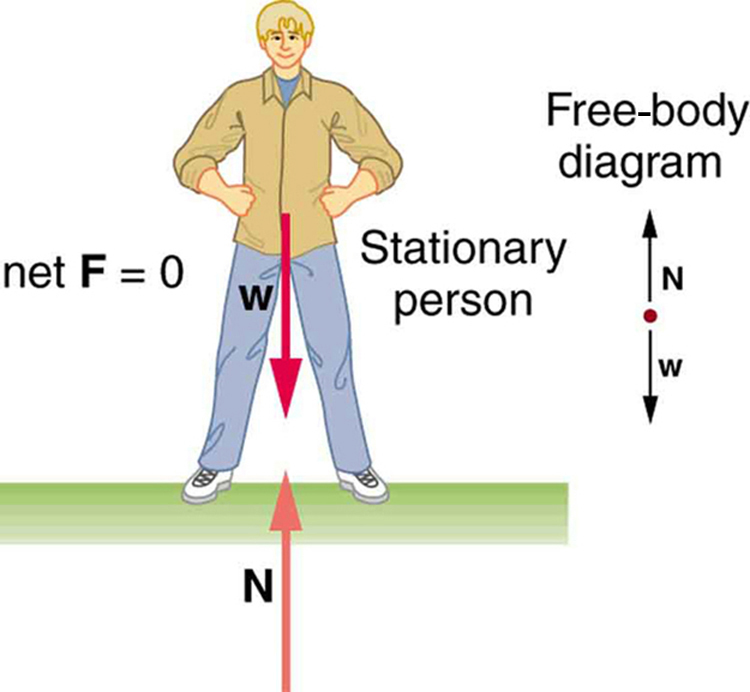
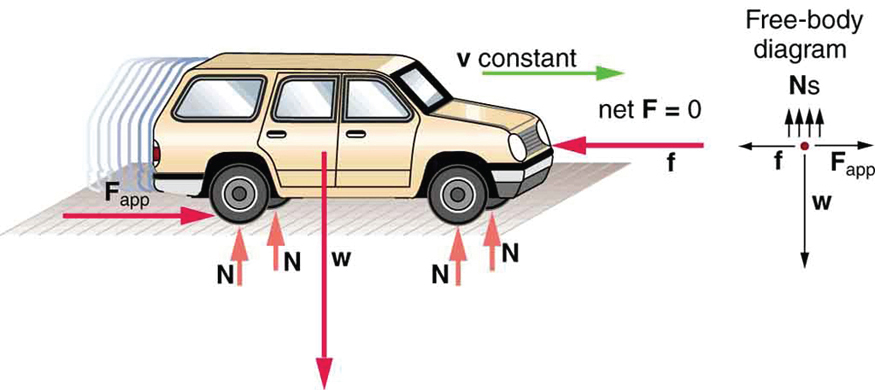
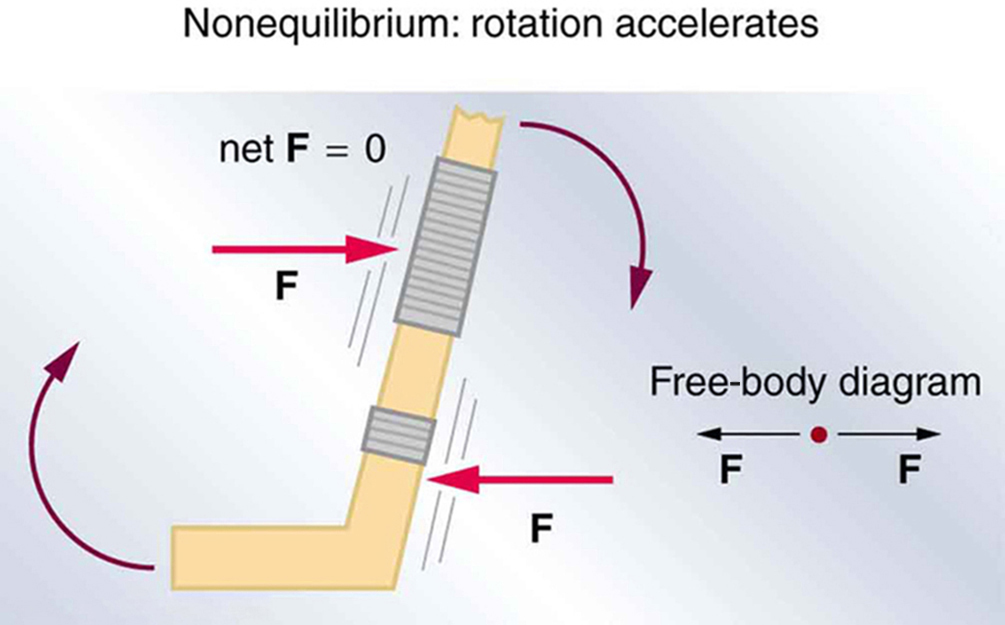
However, it is not sufficient for the net external force of a system to be zero for a system to be in equilibrium. Consider the two situations illustrated in [link] and [link] where forces are applied to an ice hockey stick lying flat on ice. The net external force is zero in both situations shown in the figure; but in one case, equilibrium is achieved, whereas in the other, it is not. In [link] , the ice hockey stick remains motionless. But in [link] , with the same forces applied in different places, the stick experiences accelerated rotation. Therefore, we know that the point at which a force is applied is another factor in determining whether or not equilibrium is achieved. This will be explored further in the next section.

Investigate how torque causes an object to rotate. Discover the relationships between angular acceleration, moment of inertia, angular momentum and torque.

What can you say about the velocity of a moving body that is in dynamic equilibrium? Draw a sketch of such a body using clearly labeled arrows to represent all external forces on the body.
Under what conditions can a rotating body be in equilibrium? Give an example.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics arranged for cpslo phys141' conversation and receive update notifications?