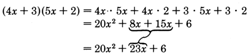This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
Factoring is an essential skill for success in algebra and higher level mathematics courses. Therefore, we have taken great care in developing the student's understanding of the factorization process. The technique is consistently illustrated by displaying an empty set of parentheses and describing the thought process used to discover the terms that are to be placed inside the parentheses.The factoring scheme for special products is presented with both verbal and symbolic descriptions, since not all students can interpret symbolic descriptions alone. Two techniques, the standard "trial and error" method, and the "collect and discard" method (a method similar to the "ac" method), are presented for factoring trinomials with leading coefficients different from 1.
Objectives of this module: be able to factor trinomials with leading coefficient other than 1.
Overview
- The Method of Factorization
The method of factorization
In the last section we saw that we could easily factor trinomials of the form
by finding the factors of the constant
that add to the coefficient of the linear term
, as shown in the following example:
Factor
.
The third term of the trinomial is
. We seek two numbers whose
(a) product is
and
(b) sum is
.
The required numbers are
and
.
The problem of factoring the polynomial
,
, becomes more involved. We will study two methods of factoring such polynomials. Each method produces the same result, and you should select the method you are most comfortable with. The first method is called the
trial and error method and requires some educated guesses. We will examine two examples (Sample Sets A and B). Then, we will study a second method of factoring. The second method is called the
collect and discard method , and it requires less guessing than the trial and error method. Sample Set C illustrates the use of the collect and discard method.
The trial and error method of factoring
Trial and error method
Consider the product
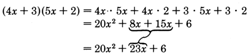
Examining the trinomial
, we can immediately see some factors of the first and last terms.
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Our goal is to choose the proper combination of factors of the first and last terms that yield the middle term
.
Notice that the middle term comes from the
sum of the
outer and
inner products in the multiplication of the two binomials.
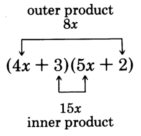
This fact provides us a way to find the proper combination.
Look for the combination that when
multiplied and then
added yields the middle term.
The proper combination we're looking for is
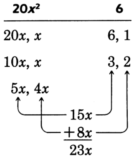
Sample set a
Factor
.
Factor the first and last terms.
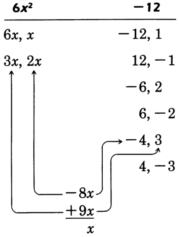
Thus,
and 3 are to be multiplied,
and
are to be multiplied.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!