| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Focusing on electrical networks, most analog ones make inefficient use of communication links because truly dynamicrouting is difficult, if not impossible, to obtain. In radio networks, such as commercial television, each station has adedicated portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and this spectrum cannot be shared with other stations or used in anyother than the regulated way. The telephone network is more dynamic, but once it establishes a call the path through thenetwork is fixed. The users of that path control its use, and may not make efficient use of it (long pauses while one personthinks, for example). Telephone network customers would be quite upset if the telephone company momentarily disconnected the pathso that someone else could use it. This kind of connection through a network—fixed for the duration of thecommunication session—is known as a circuit-switched connection.
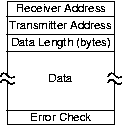
During the 1960s, it was becoming clear that not only was digital communication technically superior, but also that thewide variety of communication modes—computer login, file transfer, and electronic mail—needed a different approachthan point-to-point. The notion of computer networks was born then, and what was then called the ARPANET, now called theInternet, was born. Computer networks elaborate the basic network model by subdividing messages into smaller chunks called packets ( [link] ). The rationale for the network enforcing smaller transmissions wasthat large file transfers would consume network resources all along the route, and, because of the long transmission time, acommunication failure might require retransmission of the entire file. By creating packets, each of which has its own address andis routed independently of others, the network can better manage congestion. The analogy is that the postal service, rather thansending a long letter in the envelope you provide, opens the envelope, places each page in a separate envelope, and using theaddress on your envelope, addresses each page's envelope accordingly, and mails them separately. The network does need tomake sure packet sequence (page numbering) is maintained, and the network exit point must reassemble the original messageaccordingly.
Communications networks are now categorized according to whether they use packets or not. A system like the telephone network issaid to be circuit switched : The network establishes a fixed route that lasts the entire duration of the message. Circuit switching has theadvantage that once the route is determined, the users can use the capacity provided them however they like. Its maindisadvantage is that the users may not use their capacity efficiently, clogging network links and nodes along the way. Packet-switched networks continuously monitor network utilization, and route messages accordingly. Thus,messages can, on the average, be delivered efficiently, but the network cannot guarantee a specific amount of capacity to theusers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?