| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we continue the study of conservative vector fields. We examine the Fundamental Theorem for Line Integrals, which is a useful generalization of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to line integrals of conservative vector fields. We also discover show how to test whether a given vector field is conservative, and determine how to build a potential function for a vector field known to be conservative.
Before continuing our study of conservative vector fields, we need some geometric definitions. The theorems in the subsequent sections all rely on integrating over certain kinds of curves and regions, so we develop the definitions of those curves and regions here.
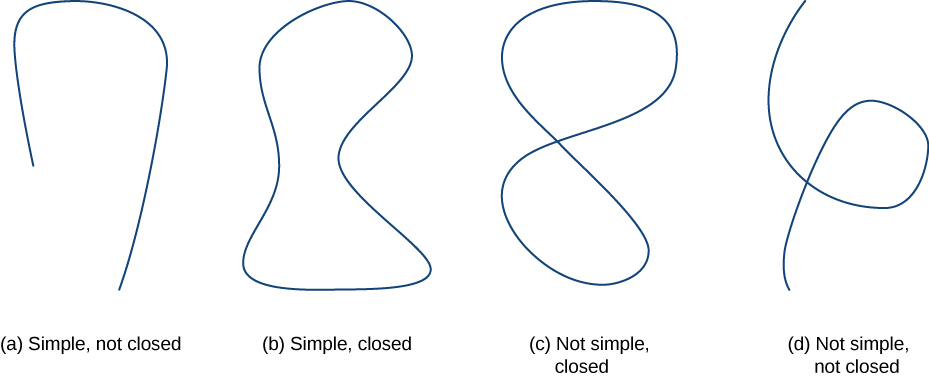
We first define two special kinds of curves: closed curves and simple curves. As we have learned, a closed curve is one that begins and ends at the same point. A simple curve is one that does not cross itself. A curve that is both closed and simple is a simple closed curve ( [link] ).
Curve C is a closed curve if there is a parameterization of C such that the parameterization traverses the curve exactly once and Curve C is a simple curve if C does not cross itself. That is, C is simple if there exists a parameterization of C such that r is one-to-one over It is possible for meaning that the simple curve is also closed.
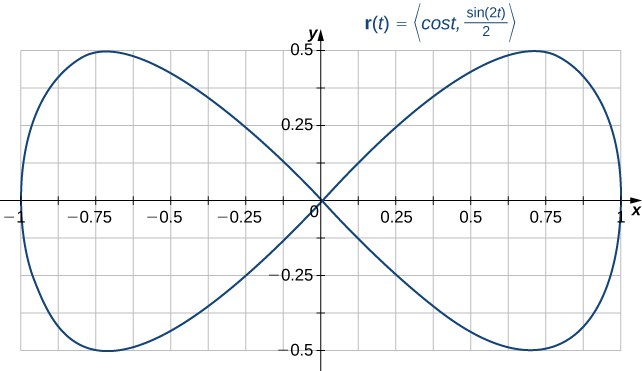
Is the curve with parameterization a simple closed curve?
Note that therefore, the curve is closed. The curve is not simple, however. To see this, note that and therefore the curve crosses itself at the origin ( [link] ).
Is the curve given by parameterization a simple closed curve?
Yes
Many of the theorems in this chapter relate an integral over a region to an integral over the boundary of the region, where the region’s boundary is a simple closed curve or a union of simple closed curves. To develop these theorems, we need two geometric definitions for regions: that of a connected region and that of a simply connected region. A connected region is one in which there is a path in the region that connects any two points that lie within that region. A simply connected region is a connected region that does not have any holes in it. These two notions, along with the notion of a simple closed curve, allow us to state several generalizations of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus later in the chapter. These two definitions are valid for regions in any number of dimensions, but we are only concerned with regions in two or three dimensions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?