| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
To start this section, we need to review some important vocabulary and notation.
Remember that when a number is multiplied by itself, we can write this as which we read aloud as For example, is read as
We call the square of because Similarly, is the square of because
If then is the square of
Do you know why we use the word square ? If we construct a square with three tiles on each side, the total number of tiles would be nine.
This is why we say that the square of three is nine.
The number is called a perfect square because it is the square of a whole number.
The chart shows the squares of the counting numbers through You can refer to it to help you identify the perfect squares.

A perfect square is the square of a whole number.
What happens when you square a negative number?
When we multiply two negative numbers, the product is always positive. So, the square of a negative number is always positive.
The chart shows the squares of the negative integers from to

Did you notice that these squares are the same as the squares of the positive numbers?
Sometimes we will need to look at the relationship between numbers and their squares in reverse. Because we say is the square of We can also say that is a square root of
A number whose square is is called a square root of
If then is a square root of
Notice also, so is also a square root of Therefore, both and are square roots of
So, every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
What if we only want the positive square root of a positive number? The radical sign, stands for the positive square root. The positive square root is also called the principal square root .
is read as “the square root of
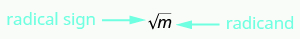
We can also use the radical sign for the square root of zero. Because Notice that zero has only one square root.
The chart shows the square roots of the first perfect square numbers.

Every positive number has two square root s and the radical sign indicates the positive one. We write If we want to find the negative square root of a number, we place a negative in front of the radical sign. For example,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?