| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Illustrate the uniform distribution . The data that follows are a random sample of 55 smiling times, in seconds, of an eight-week old baby.
| 10.4 | 19.6 | 18.8 | 13.9 | 17.8 | 16.8 | 21.6 | 17.9 | 12.5 | 11.1 | 4.9 |
| 12.8 | 14.8 | 22.8 | 20.0 | 15.9 | 16.3 | 13.4 | 17.1 | 14.5 | 19.0 | 22.8 |
| 1.3 | 0.7 | 8.9 | 11.9 | 10.9 | 7.3 | 5.9 | 3.7 | 17.9 | 19.2 | 9.8 |
| 5.8 | 6.9 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 21.7 | 11.8 | 3.4 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 6.3 | 10.7 |
| 8.9 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 7.6 | 10.0 | 3.3 | 6.7 | 7.8 | 11.6 | 13.8 | 18.6 |
sample mean = 11.49 and sample standard deviation = 6.23
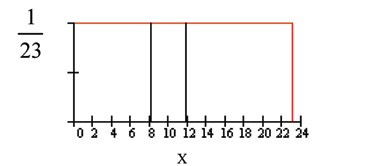
We will assume that the sample of smiling times is drawn from a population that follows a uniform distribution between 0 and 23 seconds. This means that any smiling time between 0 and 23 seconds is equally likely.
Let = length of time, in seconds, of an eight-week old's smile.
The notation for the uniform distribution is
~ where = the lowest value and = the highest value.
For this example, ~ . .
Formulas for the theoretical mean and standard deviation are
and
For this problem, the theoretical mean and standard deviation are
seconds and seconds
Notice that the theoretical mean and standard deviation are close to the sample mean and standard deviation.
To find :
What is the probability that a randomly chosen eight-week old smiles between 2 and 18 seconds?
Find .
.
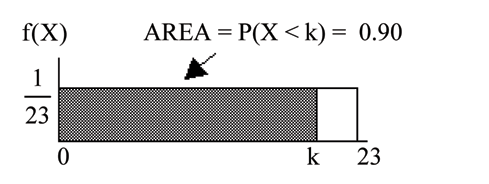
Find the 90th percentile for an eight week old's smiling time.
Ninety percent of the smiling times fall below the 90th percentile, , so
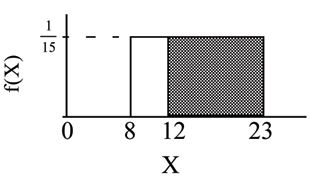
Find the probability that a random eight week old smiles more than 12 seconds KNOWING that the baby smiles MORE THAN 8 SECONDS .
Find There are two ways to do the problem. For the first way , use the fact that this is a conditional and changes the sample space. The graph illustrates the new sample space. You already know the baby smiled morethan 8 seconds.
Write a new :
for
For the second way, use the conditional formula from Chapter 3 with the original distribution ~ :
For this problem, is and is .
So,
Uniform : The amount of time, in minutes, that a person must wait for a bus is uniformly distributed between 0 and 15 minutes.
What is the probability that a person waits fewer than 12.5 minutes?
Let = the number of minutes a person must wait for a bus. = 0 and = 15. . Write the probability density function. for
Find . Draw a graph.
The probability a person waits less than 12.5 minutes is 0.8333.

On the average, how long must a person wait?
Find the mean, , and the standard deviation, .
. On the average, a person must wait 7.5 minutes.
. The Standard deviation is 4.3 minutes.
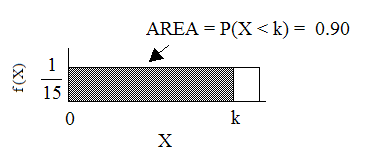
Ninety percent of the time, the time a person must wait falls below what value?
Find the 90th percentile. Draw a graph. Let = the 90th percentile.
is sometimes called a critical value.
The 90th percentile is 13.5 minutes. Ninety percent of the time, a person must wait at most 13.5 minutes.
Uniform : Ace Heating and Air Conditioning Service finds that the amount of time a repairman needs to fix a furnace is uniformly distributed between 1.5 and 4 hours. Let = the time needed to fix a furnace. Then ~ .
Find the probability that a randomly selected furnace repair requires longer than 2 hours.
To find : so
P(X>2) = (base)(height) = (4 − 2)(0.4) = 0.8
Example 4 figure 1
Find the probability that a randomly selected furnace repair requires less than 3 hours. Describe how the graph differs from the graph in the first part of this example.
= (base)(height) = (3 − 1.5)(0.4) = 0.6
The graph of the rectangle showing the entire distribution would remain the same. However the graph should be shaded between X=1.5 and X=3. Note that the shaded area starts at X=1.5 rather than at X=0; since X~U(1.5,4), X can not be less than 1.5.
Example 4 figure 2
Find the 30th percentile of furnace repair times.
Example 4 figure 3
The 30th percentile of repair times is 2.25 hours. 30% of repair times are 2.5 hours or less.
The longest 25% of furnace repair times take at least how long? (Find the minimum time for the longest 25% of repairs.)
Example 4 figure 4
The longest 25% of furnace repairs take at least 3.375 hours (3.375 hours or longer).
Note: Since 25% of repair times are 3.375 hours or longer, that means that 75% of repair times are 3.375 hours or less. 3.375 hours is the 75th percentile of furnace repair times.
Find the mean and standard deviation
and
hours and hours

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Collaborative statistics: custom version modified by r. bloom' conversation and receive update notifications?