| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Express the following series as a telescoping sum and evaluate its n th partial sum.
( Hint: Factor denominator and use partial fractions.)
( Hint: Look at
A general telescoping series is one in which all but the first few terms cancel out after summing a given number of successive terms.
in which as Find
Suppose that where as Find a condition on the coefficients that make this a general telescoping series.
Evaluate ( Hint:
Find a formula for where is a positive integer.
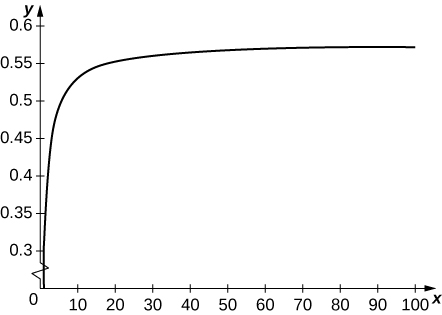
[T] Define a sequence Use the graph of to verify that is increasing. Plot for and state whether it appears that the sequence converges.
converges to
is a sum of rectangles of height
over the interval
which lie above the graph of
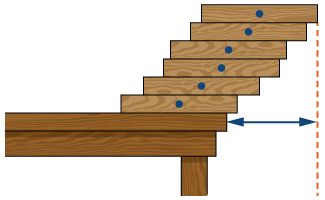
[T] Suppose that equal uniform rectangular blocks are stacked one on top of the other, allowing for some overhang. Archimedes’ law of the lever implies that the stack of blocks is stable as long as the center of mass of the top blocks lies at the edge of the bottom block. Let denote the position of the edge of the bottom block, and think of its position as relative to the center of the next-to-bottom block. This implies that or Use this expression to compute the maximum overhang (the position of the edge of the top block over the edge of the bottom block.) See the following figure.
Each of the following infinite series converges to the given multiple of or
In each case, find the minimum value of such that the partial sum of the series accurately approximates the left-hand side to the given number of decimal places, and give the desired approximate value. Up to decimals place,
[T] error
[T] error
[T] A fair coin is one that has probability of coming up heads when flipped.
a. The probability of any given ordered sequence of outcomes for coin flips is b. The probability of coming up heads for the first time on the th flip is the probability of the sequence which is The probability of coming up heads for the first time on an even flip is or

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?