| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
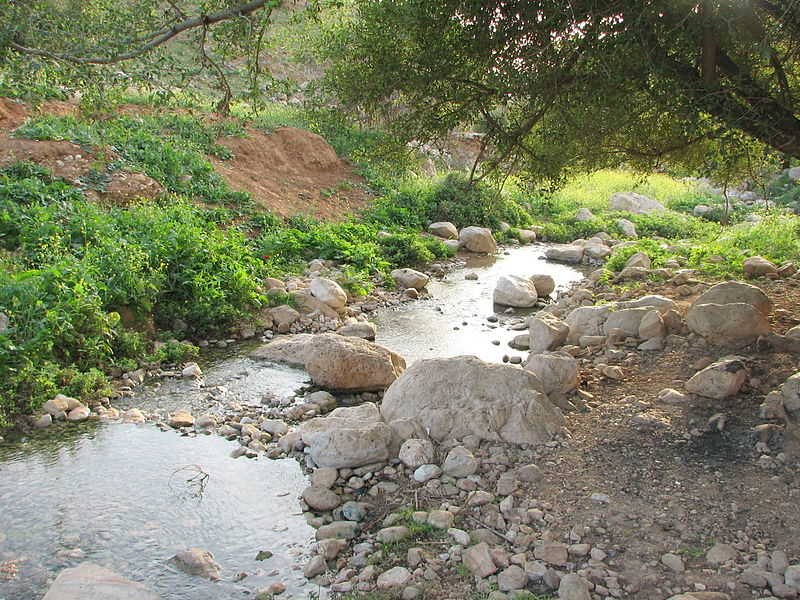
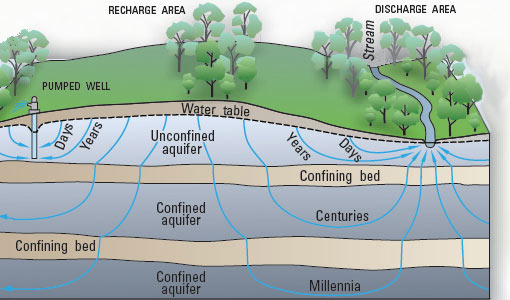

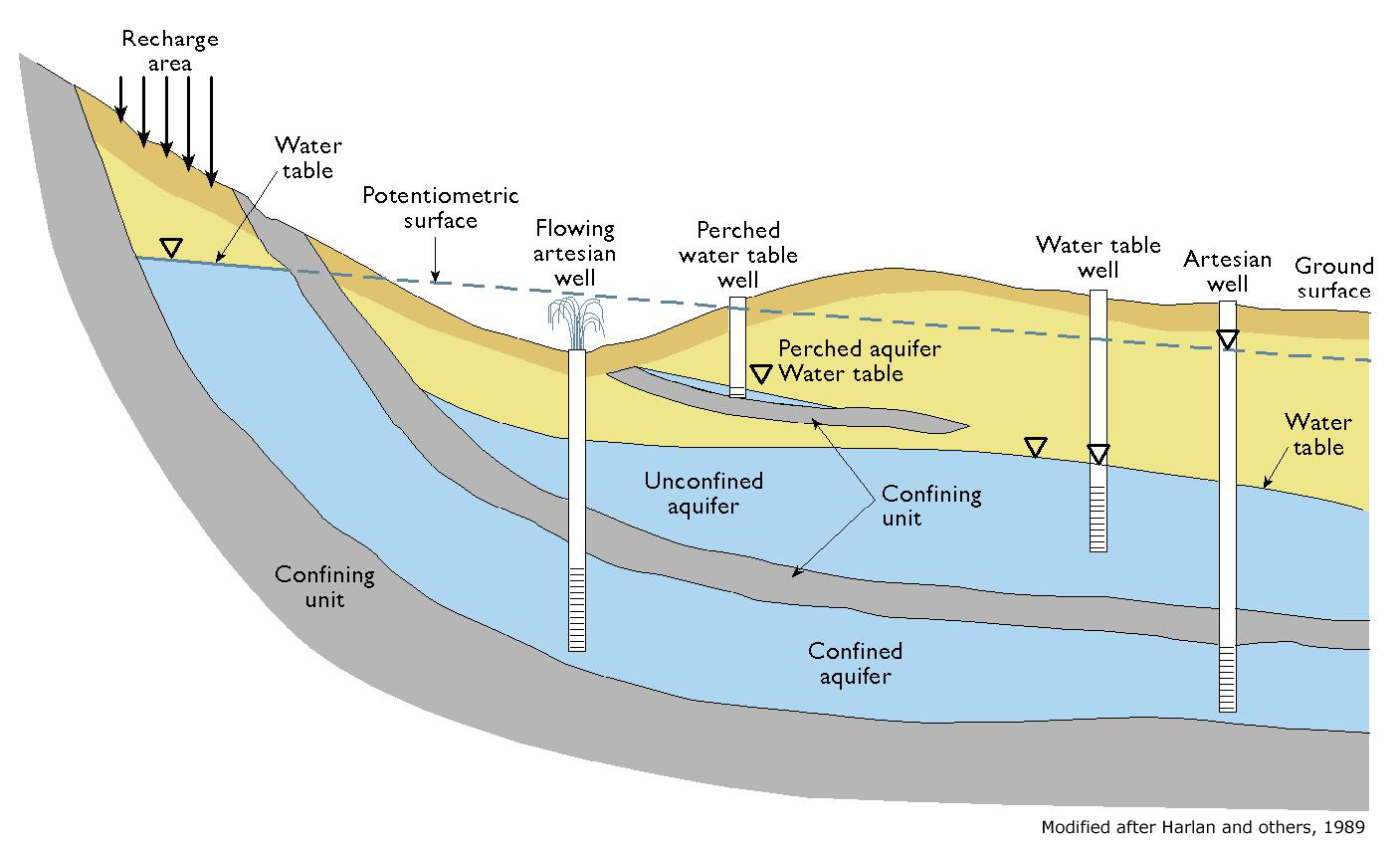
Most shallow water wells are drilled into unconfined aquifers. These are called water table wells because the water level in the well coincides with the water table (See Figure Schematic Cross Section of Aquifer Types ). 90% of all aquifers for water supply are unconfined aquifers composed of sand or gravel. To produce water from a well, you simply need to drill a hole that reaches the saturated zone and then pump water to the surface. Attempting to pump water from the unsaturated zone is like drinking root beer with a straw immersed only in the foam at the top.
To find a large aquifer for a city, hydrogeologists (geologists who specialize in groundwater) use a variety of information including knowledge of earth materials at the surface and sub-surface as well as test wells. Some people search for water by dowsing, where someone holds a forked stick or wire (called a divining rod) while walking over an area. The stick supposedly rotates or deflects downward when the dowser passes over water. Controlled tests show that a dowser's success is equal to or less than random chance. Nevertheless, in many areas water wells are still drilled on dowser’s advice sometimes for considerable money. There is no scientific basis to dowsing.
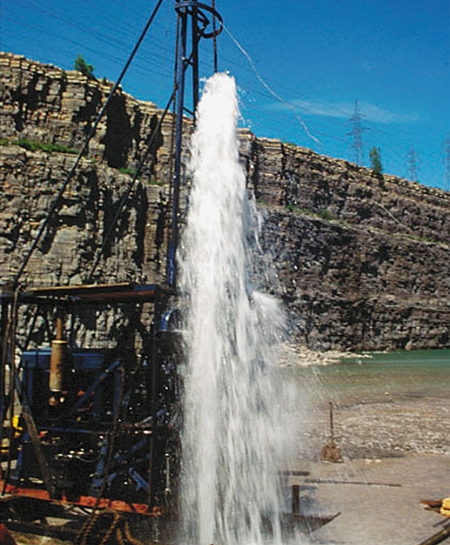
Wells into confined aquifers typically are deeper than those into unconfined aquifers because they must penetrate a confining layer. The water level in a well drilled into a confined aquifer, which is an artesian well , (see Figure Schematic Cross Section of Aquifer Types ), moves above the local water table to a level called the potentiometric surface because of the greater pressure on the groundwater. Water in a flowing well (see Figure A Flowing Well ) moves all of the way to the land surface without pumping.

A confined aquifer tends to be depleted from groundwater pumping more quickly than an unconfined aquifer, assuming similar aquifer properties and precipitation levels. This is because confined aquifers have smaller recharge areas, which may be far from the pumping well. Conversely, an unconfined aquifer tends to be more susceptible to pollution because it is hydrologically connected to the surface, which is the source of most pollution.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?