| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1.
1.1 Equally from centre
2.
2.1 180
2.2 1
2.3 360
Looking at circles:
1. Have a good look at the sketch and then answer the questions:

RQ = Diameter
SP = Radius
1.1 What is a circle?
_____________________________________________________________________
1.2 Where do we come across circles in our daily lives?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2. Answer the following questions:
2.1 How many diameters could a circle have? _____________________________
2.2 How many centre points could a circle have? __________________________
2.3 How many radii could a circle have? ________________________________
3. Use a pair of compasses and draw a circle with a:
3.1 radius of 30 mm:
3.2 diameter of 80 mm:
DID YOU KNOW?
We can draw lovely patterns based on circles! The pattern shown
below is known as a paisley design and is used on cloth or clothing.

4. Can you find out how the pattern is created? Try to do it yourself!
5. Follow the steps and use this method for drawing the patterns that follow. Your educator will provide the paper that you need.
Draw a circle Use the same radius for marking the circumference Connect the points (if necessary)
Draw a circle
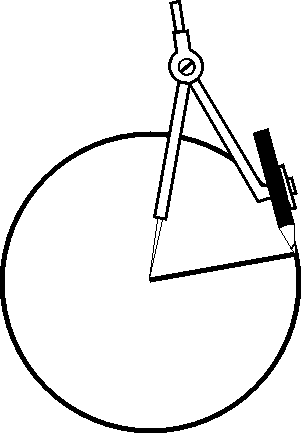
Use the same radius for marking the circumference
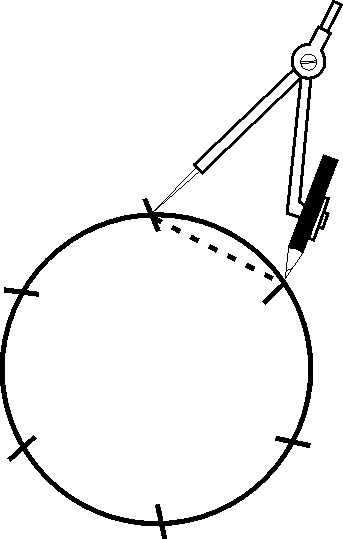
Connect the points (if necessary)

5.1

5.2

5.3

5.4

6. Design your own pattern with circles. Colour it neatly:
Time for self-assessment
It is important to know how well you understand the work that we have done up to now. Read the following criteria. Evaluate yourself on a scale ranging from 1 to 4 by circling the appropriate number.
| Criteria | 1 = Not at all.2 = Just a little.3 = Well.4 = Very well. | ||||
| I can explain the term "parallel". | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can explain the difference between a line and a line segment. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can explain the following concepts: | |||||
| * acute angle; | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| * obtuse angle; | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| * right angle. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can use a protractor to: | |||||
| * measure angles accurately; | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| * draw angles accurately. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can name the similarities between a rectangle and a parallelogram | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can name the differences between a rectangle and a parallelogram. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can explain the concept "symmetrical". | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can explain the concept "rotational symmetry". | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can explain the following concepts: | |||||
| * radius; | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| * diameter. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I could enlarge and reduce the figures. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| I can use circles to draw patterns. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
Let's look at 3-dimensional figures.
You probably quite often play games that require a die. See if you can make one yourself. Trace the outlines of the following net exactly. Cut it out neatly and fold it to form a die. Then write the numbers 1 to 6 on the sides. Remember that the numbers of the following number pairs (1,6), (3,4) and (2,5) must be on opposite sides.

DID YOU KNOW?
The die that you have just made is an example of a cube.
Take a good look at the following:

Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner investigates and compares (alone or as a member of a group or team) two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects studied in this grade according to properties listed above by:
3.3.3: using a pair of compasses to draw circles, patterns in circles, and patterns with circles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?