This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
Operations with algebraic expressions and numerical evaluations are introduced in this chapter. Coefficients are described rather than merely defined. Special binomial products have both literal and symbolic explanations and since they occur so frequently in mathematics, we have been careful to help the student remember them. In each example problem, the student is "talked" through the symbolic form.Objectives of this module: be able to expand (a + b)^2, (a - b)^2, and (a + b)(a - b).
Overview
- Expanding
and
- Expanding
Three binomial products occur so frequently in algebra that we designate them as
special binomial products . We have seen them before (Sections
[link] and
[link] ), but we will study them again because of their importance as time saving devices and in solving equations (which we will study in a later chapter).
These special products can be shown as the
squares of a binomial
and
and as the
sum and difference of two terms .
There are two simple rules that allow us to easily expand (multiply out) these binomials. They are well worth memorizing, as they will save a lot of time in the future.
Expanding
And
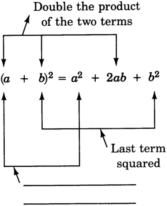
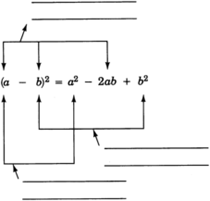
Squaring a binomial
To square a binomial:
- Square the first term.
- Take the product of the two terms and double it.
- Square the last term.
- Add the three results together.
Expanding
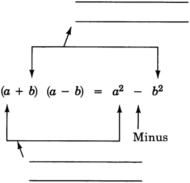
Sum and difference of two terms
To expand the sum and difference of two terms:
- Square the first term and square the second term.
- Subtract the square of the second term from the square of the first term.
See problems 56 and 57 at the end of this section.
See problem 58.
Sample set a
Note that
. The
term is missing!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Notice that the sign of the last term in this expression is “
.” This will always happen since the last term results from a number being
squared . Any nonzero number times itself is always positive.
The sign of the second term in the trinomial will always be the sign that occurs
inside the parentheses.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
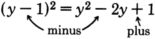
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
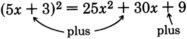
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
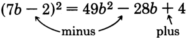
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Practice set a
Find the following products.
Exercises
For the following problems, find the products.
Exercises for review