| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes, but within the space enclosed by a chloroplast’s inner membrane is a set of interconnected and stacked, fluid-filled membrane sacs called thylakoids ( [link] ). Each stack of thylakoids is called a granum (plural = grana). The fluid enclosed by the inner membrane and surrounding the grana is called the stroma.
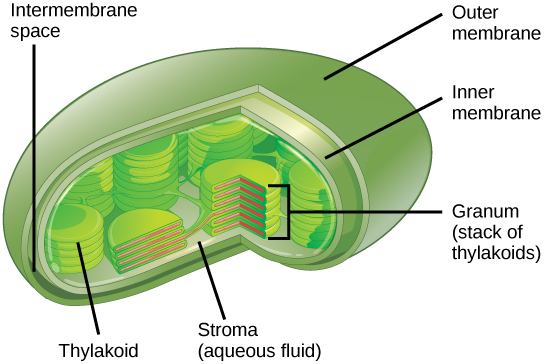
The chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which captures the energy of sunlight for photosynthesis. Like plant cells, photosynthetic protists also have chloroplasts. Some bacteria also perform photosynthesis, but they do not have chloroplasts. Their photosynthetic pigments are located in the thylakoid membrane within the cell itself.
Symbiosis is a relationship in which organisms from two separate species live in close association and typically exhibit specific adaptations to each other. Endosymbiosis ( endo- = within) is a relationship in which one organism lives inside the other. Endosymbiotic relationships abound in nature. Microbes that produce vitamin K live inside the human gut. This relationship is beneficial for us because we are unable to synthesize vitamin K. It is also beneficial for the microbes because they are protected from other organisms and are provided a stable habitat and abundant food by living within the large intestine.
Scientists have long noticed that bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are similar in size. We also know that mitochondria and chloroplasts have DNA and ribosomes, just as bacteria do. Scientists believe that host cells and bacteria formed a mutually beneficial endosymbiotic relationship when the host cells ingested aerobic bacteria and cyanobacteria but did not destroy them. Through evolution, these ingested bacteria became more specialized in their functions, with the aerobic bacteria becoming mitochondria and the photosynthetic bacteria becoming chloroplasts.
Previously, we mentioned vacuoles as essential components of plant cells. If you look at [link] , you will see that plant cells each have a large, central vacuole that occupies most of the cell. The central vacuole plays a key role in regulating the cell’s concentration of water in changing environmental conditions. In plant cells, the liquid inside the central vacuole provides turgor pressure, which is the outward pressure caused by the fluid inside the cell. Have you ever noticed that if you forget to water a plant for a few days, it wilts? That is because as the water concentration in the soil becomes lower than the water concentration in the plant, water moves out of the central vacuoles and cytoplasm and into the soil. As the central vacuole shrinks, it leaves the cell wall unsupported. This loss of support to the cell walls of a plant results in the wilted appearance. Additionally, this fluid has a very bitter taste, which discourages consumption by insects and animals. The central vacuole also functions to store proteins in developing seed cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-nya-05 - general biology i' conversation and receive update notifications?