| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
AKTIWITEIT 1:
OM 'N PLANTSEL SE BOU TE VERSTAAN
[LU 2.1; 2.2; 2.3]
Vra jou onderwyser om ‘n mosplantjieblaar of enige ander voorbeeld beskikbaar te stel vir mikroskoopstudie.
Jy sou die bou van ‘n tipiese sel kon bestudeer. Hieronder is ‘n baie vereenvoudigde lynskets en twee-dimensionele beeld van wat jy sou sien.
Die sel bestaan uit ‘n raamwerk met ‘n spesiale vloeistof – PROTOPLASMA – en verskeie strukture dryf daarin. Sommige van hulle is te klein om met ‘n gewone mikroskoop gesien te word. Daarvoor word die elektronmikroskoop gebruik. Onthou dat jy die sel slegs van een kant af sien. Dit het na regte ‘n vorm soos ‘n baksteen. Ons sê dit is drie-dimensioneel. Vra jou onderwyser om die begrip te verduidelik.
Vir verryking:
Vind meer uit oor mikroskope en elektronmikroskope.
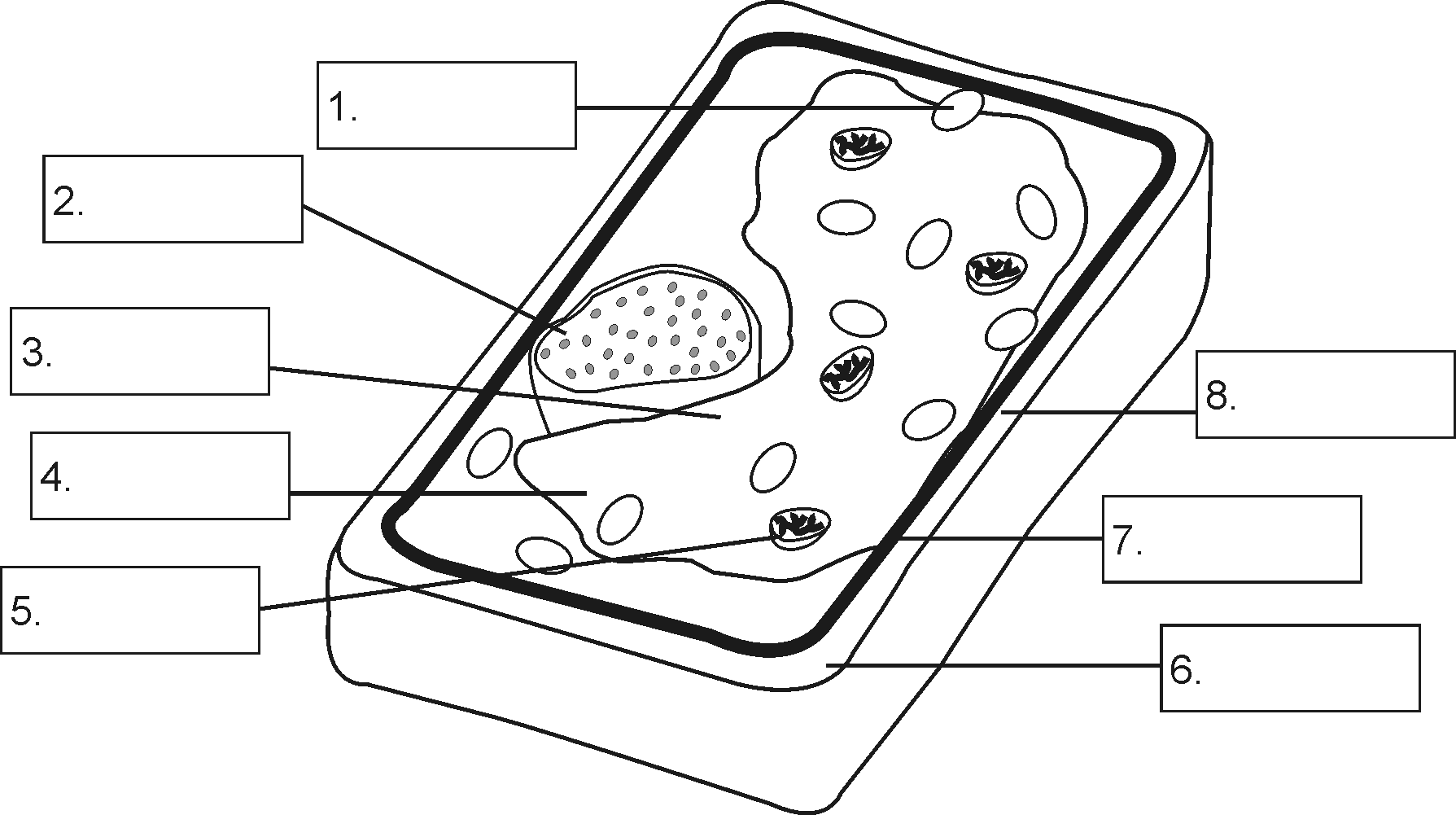
Opdrag 1:
1. Voorsien die skets van ‘n onderskrif.
2. Vul die byskrifte en funksies in waar van toepassing.
Opdrag 2:
Die kern het egter fyner besonderhede waarvan jy kennis moet dra voordat jy die res van die module doen.

Bespreek in die klas elkeen van die byskrifte van die kern en som die funksie van elkeen op.
| 1. | Nukleolus |
| 2. | Chromatiennetwerk |
| 3. | Kernmembraan |
| 4. | Kernplasma |
Wat is die hooffunksie van die kern nou weer?
Hoewel die kern die beheersentrum van die sel is, is daar nog twee ander organelle wat nadere ondersoek regverdig, aangesien hulle so ‘n belangrike funksie verrig.
Plante FOTOSINTETISEER en RESPIREER . Die twee organelle hierby betrokke is die CHLOROPLAST (fotosintese)en die MITOCHONDRIA (respirasie). Jy sal tot in Graad 12 in jou studies met hierdie organelle te doen kry.
Jou onderwyser sal meer gedetailleerde sketse van hierdie twee organelle met julle behandel.
Assessering van Identifikasie-Selstrukture
Kon jy basiese strukture onderskei?
[LU 2.1; LU 2.3]
Opdrag 3:
Maak ‘n eenvoudige lynskets met byskrifte van elk van die twee belangrike organelle in die spasies voorsien. Moenie onderskrifte vergeet nie.
Watter van die strukture en aspekte wat jy as deel van die plantsel leer ken het, sou jy nie kon verwag om in die diersel te vind nie? Gee redes:
(Wenk: kyk na jouself en na ‘n plant, en voel aan jouself en aan ‘n plant.)
Assessering van Lynsketse en Afleidings
Kon jy sketse doen en afleidings maak?
[LU 2.3; LU 2.4]
Jy verstaan nou dat plantselle bepaalde kenmerke het. Almal lyk egter nie dieselfde nie, aangesien hulle aangepas is om spesifieke funksies te verrig. Hierdie aanpassings in bou noem ons DIFFERENSIASIE en die gepaardgaande verandering in funksies noem ons SPESIALISASIE . Beide terme is belangrik in biologiese selstudies.
‘n Groep selle wat aangepas is om ‘n bepaalde funksie te verrig, vorm saam ‘n WEEFSEL . So is daar selle wat water in die plant moet vervoer. Ander bied versterking. Ander is aangepas om maksimaal te fotosintetiseer.
Die weefsels op hulle beurt groepeer weer saam om ‘n gesamentlike funksie te verrig. So ‘n struktuur, bestaande uit baie soorte plantweefsels, maar met ‘n gesamentlike hooffunksie, noem ons ‘n ORGAAN, byvoorbeeld ‘n blaar.
LU 2
Konstruksie van Wetenskapkennis
Die leerder ken, interpreteer en pas wetenskaplike, tegnologiese en omgewings- kennis toe.
Dit word bewys as die leerder:
2.1 betekenisvolle inligting kan oproep;
2.2 inligting kan kategoriseer;
2.3 inligting kan interpreteer;
2.4 kennis kan toepas.
AKTIWITEIT
OPDRAG 1
1. Lynskets van ‘n tipiese plantsel

| Byskrif-Nommer | Byskrif | Funksie |
| 1. | Chloroplast | Fotosintese vind hierin plaas |
| 2. | Kern | Beheer alle selaktiwiteite |
| 3. | Tonoplast van vakuool | Membraan om vakuool; vakuool stoor vog en kleurstowwe |
| 4. | Selsap | Vog, kleurstowwe |
| 5. | mitochondrion | Respirasie (energie “kragsentrale”) |
| 6. | Selwand | Buitenste beskermende, verstewigende wand |
| 7. | Selmembraan | Beheer in- en uitgang van stowwe |
| 8. | Sitoplasma | Medium waarin reaksies plaasvind en organelle dryf |
OPDRAG 2:
DIE KERN

| Byskrif | Funksie | |
| 1. | Nukleolus | Beheer molekule in die kern |
| 2. | Chromatiennetwerk | Stoor genetiese materiaal; dra oorerflike eienskappe |
| 3. | Kernmembraan | Hou kernmateriaal bymekaar, kommunikeer met res van sel |
| 4. | Kernplasma | Spesiale strukture en vog |
Opdrag 3
Plante FOTOSINTETISEER en RESPIREER. Die twee organelle hierby betrokke is die CHLOROPLAST en die MITOCHONDRIA . Studie van hulle is tot in matriek baie belangrik.
CHLOROPLASTE
bevat die kleurpigment chlorofil;
akkommodeer die proses van fotosintese;
het dubbele membraan rondom;
strome vloeistof en granum (grana) – hopies membrane (tilakoïede) wat daarin dryf. Grana word verbind met ander plat membrane (lamellae).
MITOCHONDRIA
akkommodeer die ENERGIE-gewende proses van RESPIRASIE;
bestaan ook uit ‘n dubbele membraan;
vou aan die binnekant word kristas (cristae) genoem;
matriks is die vloeistof aan die binnekant.
Nie al die moontlike organelle word in Gr. 9 behandel nie, maar van dié wat reeds genoem is, sal sekeres die verskille tussen tipiese plant- en dierselle aandui.
| Struktuur | Rede |
| Selwand | Afwesig in dierselle; hou vorm en gee stewigheid in plantselle, want plante het nie skelette nie. |
| Vakuool | Klein of afwesig by dierselle; hulle stoor en gee ook stewigheid in plantselle. |
| Chloroplaste | Geen PLASTIEDE kom in dierselle voor nie. |
| Vaste vorm | Plantselle het ‘n vaste vorm a.g.v. die selwand – dierselle het baie vorme. |
Jy verstaan nou dat plantselle uniek is. In die natuur is daar egter baie variasie op die vorm en eienskappe van plantselle. Hierdie verandering in bou noem ons DIFFERENSIASIE en daarmee saam gaan verandering in funksie wat ons SPESIALISASIE noem beide terme is uiters belangrik in biologiese selstudies.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natuurwetenskappe graad 9' conversation and receive update notifications?