| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. Scale and calculating distance
1.1 Scale
Scale refers to how much smaller the map is than the actual earth area of the earth surface that is represented. You have already learnt about the different kinds of scale that are used:
a) The word scale expresses the scale in words, e.g. “One centimetre represents half a kilometre.”
b) The ratio scale is written as a ratio or a fraction,e.g. 1:50 000 or
This means that one unit (e.g. cm) on the map represents 50 000 of the same unit (cm) of the earth surface.
c) The linear scale is a line marked off in centimetres to indicate a corresponding distance on the earth in kilometres.

Distance shown as 3,5 km
1.1.1 Measuring distance on a map
We will be making use of the topographic map series drawn to the scale of 1:50 000 throughout.
Work in the following manner to determine distance:
Use a ruler to measure the distance on the map accurately in centimetres.
Convert the distance to km or m , depending on what is required.
Example:
A_____________________________B
Scale 1:50 000
The map distance between A and B is 10 cm.
What is the actual distance in km?
10 cm × 50 000
500 000 cm ÷ 100 000
= 5 km
What is the actual distance in m?
10 cm × 50 000
500 000 cm ÷ 100
= 5 000 m
Why do we divide by 100 000 and by 100?
The metric units of measurement can be represented as follows:
| Km | Hm | Dm | M | dm | cm | mm |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
We therefore have 100 000 cm in ’n km 100 cm in ’n metre
You may use a shorter method, if you can remember that the scale of 1:50 000 is the same as:
Now calculate the distance as follows:
10 cm × 0,5
= 5 km
10 cm × 500
= 500 m
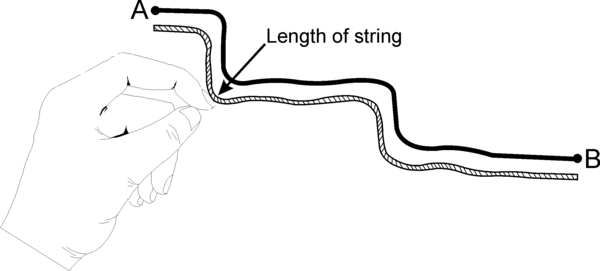
If a meandering road has to be measured, the route should first be measured by laying a piece of string along is representation. Then measure the length of the string against a ruler and then use the method suggested above, or the linear scale.
ACTIVITY:
1. Calculate the actual distance in metres if the distance on the 1:50 000 topographic map is as follows:
a) 2,3 cm
b) 6,8 cm
c) 5,5 cm
2. Calculate the actual distance in kilometres if the distance on the 1:50 000 topographic map is as follows:
a) 90,4 cm
b) 56,3 cm
c) 103,6 cm
3. Study the 1:50 000 topographical map of Beaufort West and answer the following questions:
a) What is the distance (as the crow flies) in km from Grootplaat (32º16’15”S; 22º34’36”E) to Lammertjiesleegte (spot height 881) (32º19’50” S; 22º32’50” E)?
b) How far will you travel (on the N1) in your car from the Motel (32º20’00”S; 22º35’09”E) to the train bridge (32º21’48” S; 22º33’43”E).
c) What is the distance in metres of the Springfontein dam wall? (33º20’39”S; 22º35’08”E)
[LO 1.3]
| Learning Outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| Geographical EnquiryThe learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and environmental concepts and processes. |
| Assessment Standards(ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
|
|
|
|
ACTIVITY:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Geography grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?