| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We will start by taking a walk through an optimizing compiler to see one at work. We think it’s interesting, and if you can empathize with the compiler, you will be a better programmer; you will know what the compiler wants from you, and what it can do on its own.
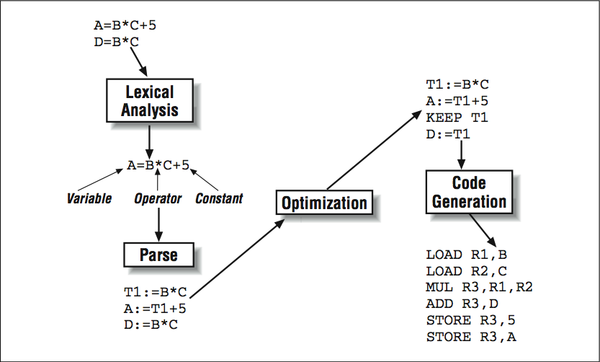
The compilation process is typically broken down into a number of identifiable steps, as shown in [link] . While not all compilers are implemented in exactly this way, it helps to understand the different functions a compiler must perform:
As compilers become more and more sophisticated in order to wring the last bit of performance from the processor, some of these steps (especially the optimization and code-generation steps) become more and more blurred. In this chapter, we focus on the traditional optimizing compiler, and in later chapters we will look more closely at how modern compilers do more sophisticated optimizations.
Because we are most interested in the optimization of our program, we start our discussion at the output of the parse phase of the compiler. The parse phase output is in the form of an an intermediate language (IL) that is somewhere between a high-level language and assembly language. The intermediate language expresses the same calculations that were in the original program, in a form the compiler can manipulate more easily. Furthermore, instructions that aren’t present in the source, such as address expressions for array references, become visible along with the rest of the program, making them subject to optimizations too.
How would an intermediate language look? In terms of complexity, it’s similar to assembly code but not so simple that the definitions By “definitions,” we mean the assignment of values: not declarations. and uses of variables are lost. We’ll need definition and use information to analyze the flow of data through the program. Typically, calculations are expressed as a stream of quadruples — statements with exactly one operator, (up to) two operands, and a result. More generally, code can be cast as n -tuples. It depends on the level of the intermediate language. Presuming that anything in the original source program can be recast in terms of quadruples, we have a usable intermediate language. To give you an idea of how this works, We’re going to rewrite the statement below as a series of four quadruples:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'High performance computing' conversation and receive update notifications?