| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
13.4
| a) | 2 | 2,60 |
| b) | 13 | 13,625 |
| c) | 17 | 17,75 |
| d) | 23 | 23,875 |
| e) | 36 | 36,8 |
13.5 a) 0,83
13.6
| 4 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 25 | 4 | 39 |
| 4,5 | 5,5 | 3,25 | 8,6 | 25,125 | 4,056 | 39,8 |
14. a) 0,3
We can convert proper fractions to decimal fractions in this way:

13.2 Did you know?
We can also calculate it in this way:
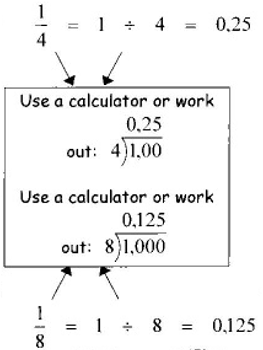
13.3 Which of the methods shown above do you choose?
Why?
13.4 Complete the following tables:

13.5 Use the division method as shown in 13.2 and write the following fractions as decimal fractions:
a) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
b) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
c) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
d) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
13.6 Can you complete the following table??
| Improper fraction | |||||||
| Mixed Number | |||||||
| Decimal fraction | 3,25 | 4,056 |
14. BRAIN-TEASERS!
Write the following fractions as decimal fractions. Try to do these sums first without a calculator!
a) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
b) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
c) ........................................................................... ...........................................................................
...........................................................................
15. Do you still remember?
We call 0,666666666 . . . a recurring decimal . We write it as .
0,454545 . . . is also a recurring decimal and we write it as .
We normally round off these recurring decimals to the first or second decimal place, e.g.: becomes 0,7 or 0,67 and becomes 0,5 or 0,45
16. Time for self-assessment
|
YES | NO | |
| I can: | |||
| Compare decimal fractions with each other and put them in the correct sequence. | |||
| Fill in the correct relationship signs. | |||
| Round off decimal fractions correctly to: | |||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| Convert fractions and improper fractions correctly to decimal fractions. | |||
| Explain what a recurring decimal is. |
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.4: We know this when the learner recognises and uses equivalent forms of the rational numbers listed above, including:
1.4.2 decimals;
Assessment Standard 1.10: We know this when the learner uses a range of strategies to check solutions and judges the reasonableness of solutions.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner represents and uses relationships between variables in a variety of ways using:
2.3.1 verbal descriptions;
2.3.3 tables.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?