| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
SSPD_Chapter 1_Part 8_continued_AN ELECTRON IN A POTENTIAL WELL OF FINITE HEIGHT AND FINITE WIDTH – QUANTUM MECHANICAL TUNNELING.

Fig(1.30) Depiction of quantum mechanical tunneling in a potential well of finite width.
Classically an electron trapped in a potential well cannot come out of it unless it has sufficient energy to cross the potential barrier confining the electron in a potential well. In photo-ionic emission as already seen and in thermo-ionic emission as we will see in the second chapter, when the photon energy imparted or thermal energy acquired exceeds the work function = qφ surface (where φ surface is the surface barrier potential) then only electron escapes into vacuum from the cathode electrode. But for an electron trapped in a potential well there is a finite probability that the electron will appear outside the well if the potential barrier is sufficiently thin. This phenomena is known as quantum mechanical tunneling.
In Fig(1.30), the phenomena of quantum mechanical tunneling is illustrated.
Within the well electron exists as a standing wave . Outside the well the electron exists as a traveling wave.
On the right of the well it exists as a forward traveling wave and on the left of the well it exists as a backward traveling wave.
For the mathematical simplicity we analyze an electron tunneling through a finite width potential barrier of finite height as depicted in Fig(1.31). The electron is travelling from left to right.
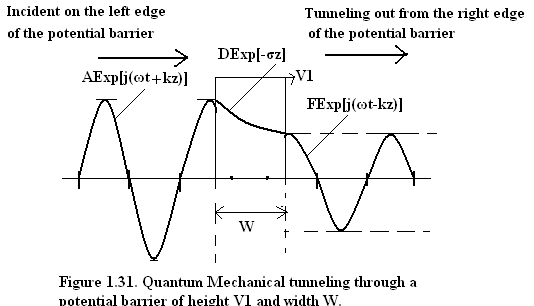
Fig(1.31) Quantum Mechanical Tunneling of Potential Barrier of height V 1 and width W.
According to Fig(1.31) the Schrodinger Equation on the left is:
∂ 2 ψ /∂z 2 + (2mE/ћ 2 )ψ = 0
The wave vectors are k 1 and k 1 * = ± i[√(2mE)]/ћ
And the solution is: ψ I = AExp[i(ωt + |k 1 |z )] + B. Exp[i(ωt - |k 1 |z )] 1.68
Eq.(1.68) is a combination of forward and backward traveling waves.
Inside the potential barrier:
∂ 2 ψ /∂z 2 - {2m(qV 1 -E)/ћ 2 }ψ = 0
The roots of the characteristic equation are real hence the roots are the attenuation coefficients: σ 1 = [√(2m(qV 1 -E)]/ћ and σ 2 = -[√(2m(qV 1 -E)]/ћ = -σ 1 ;
And the solution is: ψ II = [C.Exp(σ 1 z) + D.Exp(-σ 1 z)]Exp[i(ωt)]1.69
Eq.(1.69) is not a traveling wave but a combination of exponentially decaying and exponentially growing function out of which exponentially growing term is technically not feasible.
On the right of the barrier:
∂ 2 ψ /∂z 2 + (2mE/ћ 2 )ψ = 0
The wave vectors are again k 1 and k 1 * = ± i[√(2mE)]/ћ
And the solution is: ψ III = E.Exp[i(ωt + |k 1 |z )] + F. Exp[i(ωt - |k 1 |z )] 1.70
According to the boundary conditions: ψ I (x=0) = ψ II (x=0);
ψ II (x=W) = ψ III (x=W);
For the continuity of the wave function at the boundary we have:
∂ψ I /∂z|(x=0) = ∂ψ II /∂z|(x=0);
∂ψ II /∂z |(x=W) = ∂ψ III /∂z|(x=W); 1.71
Applying the above boundary conditions to the three solutions of the Schrodinger Equations we get the following:
ψ I = AExp[i(ωt + |k 1 |z )] – Forward traveling wave incident on the barrier from the left;
ψ II = [D.Exp(-σ 1 z)]Exp[i(ωt)]- Exponentially decaying function within the barrier;
ψ III = F. Exp[i(ωt - |k 1 |z )]- Transmitted traveling wave on the right of the barrier after quantum mechanical tunneling;
Also A = D and F = D.Exp(-σ 1 W) 1.72
|A| 2 = probability density of the incident electron wave;
|F| 2 = probability density of the transmitted wave;
Therefore quantum tunneling ratio =
T=|F| 2 /|A| 2 =Exp[-2W{√(2m e (qV 1 -E))}/ћ] 1.73
This Eq.(1.73) establishes that if W is thin enough of the order of 10Å and (qV 1 -E) of the order of 1eV (this is the order of built-in barrier potential at a pn junction then T is a finite quantity and quantum mechanical tunneling has good probability of occurring.
In Table (1.4) tunneling ratio is tabulated for different potential height and different potential widths.
Table 1.4. Quantum Mechanical Tunneling Ratio .
| Width of the barrier(W) Å | (qV 1 -E) eV | T |
| 10 | 1 | 3.5×10 -5 |
| 5 | 1 | 6×10 -3 |
| 1 | 1 | 0.36 |
| 1 | 10 | 0.04 |
| 1 | 100 | 3.5×10 -5 |
Tunneling ratio 3.5×10 -5 implies that in a potential barrier width of 10 Å and (V 1 -E) =1V out of 10 5 incident electrons 3.5 electrons will tunnel through. If the potential barrier width is reduced to 1 Å and barrier height is (V 1 -E) =1V then almost 36% of the incident electrons will tunnel through.
Tunnel Diode, Backward Diode, Zener Diode as well as high field emission utilizes quantum mechanical tunneling phenomena. In 1957 , Esaki [Appendix XXXV ] invented the first quantum device namely Tunnel Diode. At University of Cambridge, Brian Josephson [Appendix XXXVI ] adapted Tunnel Diode to superconducting materials giving rise to Josephson effect. For the invention of Tunnel Diode Brian Josephson (England), Leo Esaki (Japan) and Evar Gebar (USA) were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in the year 1973. In honour of Leo Esaki, Tunnel Diode was named as Esaki Diode.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Solid state physics and devices-the harbinger of third wave of civilization' conversation and receive update notifications?