| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1 LOG_printf(&trace,"TSK0 Start");
In the table, the TSK0 is in the TSK_RUNNING (E) state, TSK1 is in the TSK_READY (R) state, the semaphore has a value of 1 and the line causes the output "TSK0 Start". The next line of code to execute is
2 SEM_pend(&SEM0,SYS_FOREVER);
The other states for the tasks are TSK_BLOCKED (B) and TSK_TERMINATED (T).
| Code Line # | TSK0 State | TSK1 State | SEM0 | Output |
| 1 | E | R | 1 | TSK0 Start |
| 2 | E | R | 0 | |
| 3 | E | R | 0 | TSK0 1 |
| 4 | B | E | 0 | |
| 5 | B | E | 0 | TSK1 Start |
| 6 | R | E | 0 | |
| 7 | R | E | 0 | TSK 1 |
| 8 | R | E | 1 | |
| 9 | R | E | 0 | |
| 10 | E | B | 0 | |
| 11 | E | B | 0 | TSK0 2 |
| 12 | E | R | 0 | |
| 13 | E | R | 1 | |
| 14 | E | R | 1 | TSK0 3 |
| 15 | E | R | 2 | |
| 16 | E | R | 2 | TSK0 Finish |
| 17 | T | E | 2 | TSK1 2 |
| 18 | T | T | 2 | TSK1 Finish |
There are a couple common practical uses for semaphores. One of those uses is to count how many items are on a queue. The other is to restrict tasks from accessing a resource at the same time.
Suppose there are two tasks in your system, TSK_Send and TSK_Receive and there is one queue between them, QUE0. To keep track of how many elements are on the queue there is a counting semaphore, SEM0. The semaphore is initialized to 0. See Figure 1.
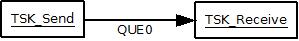
When TSK_Send puts a message on the queue, it will perform a
SEM_post(&SEM0) which will increment the count on the semaphore. Before the TSK_Receive tries to get a message off the queue it will perform a
SEM_pend(&SEM0,SYS_FOREVER) . This will decrement the count on the semaphore every time the TSK_Receive takes a message off the queue. If there are no messages on the queue, SEM0 will be 0 and the task will block. This will cause the task to wait until the TSK_Send task puts another message on the queue.
When two tasks share a resource, it may be necessary for the tasks have mutually exclusive access to the resource. In this case, a semaphore can be used to acquire access to the resourse or lock access to a resource.
Suppose there are two tasks with the same priority in your system, TSK0 and TSK1. There is a Resource that the two tasks share. A semaphore, SEM0, will be used to aquire access to the resource. The semaphore is initialized to 1. See Figure 2.

In order for the tasks to have mutually exclusive access to the resource, each task must perform a
SEM_pend(&SEM0,SYS_FOREVER) before using the resource and a
SEM_post(&SEM0) after using the resource.
Examine the following code that does NOT use a semaphore when writing to the resource.
int Resource[4];Void funTSK0()
{Resource[0]=0;Resource[1]=1;TSK_yield();
Resource[2]=2;
Resource[3]=3;
}Void funTSK1(){
Resource[0]=4;
Resource[1]=5;
Resource[2]=6;
Resource[3]=7;
}
When the tasks finish the contents of the array Resource will be [4,5,2,3]. Clearly, we would like it to be either [0,1,2,3]or [4,5,6,7]. To fix this, add the semaphore.
int Resource[4];Void funTSK0()
{SEM_pend(&SEM0,SYS_FOREVER);
Resource[0]=0;
Resource[1]=1;
TSK_yield();Resource[2]=2;Resource[3]=3;SEM_post(&SEM0);
}Void funTSK1(){
SEM_pend(&SEM0,SYS_FOREVER);
Resource[0]=4;
Resource[1]=5;
Resource[2]=6;
Resource[3]=7;
SEM_post(&SEM0);
}
When the tasks finish the contents of the array Resource will be [4,5,6,7]. The reason for this is that after TSK0 performs a
TSK_yield , TSK1 tries to perform a
SEM_pend but gets blocked. At that point TSK0 continues running and finishes with the resource. Then TSK1 begins to run and writes the complete array.
Whe debugging a project it is important to see the characteristics of the components in your project. When using DSP/BIOS in CCS it is possible to view the DSP/BIOS objects and their properties using the RTSC Object Viewer (ROV). RTSC is Real Time Software Components which is a standard for developing software modules/libraries.
To view the DSP/BIOS v5.x objects and properties in the debug mode, select Tools->ROV . This will bring up a window that looks like the following figure.

This figure shows the SEM module and the semaphore in the project. Notice the different properties that can be seen for each semaphore.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ti dsp/bios lab' conversation and receive update notifications?