| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The elementary circuit elements—the resistor,capacitor, and inductor— impose linear relationships between voltage and current.
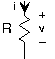
The resistor is far and away the simplest circuit element. In a resistor, the voltage is proportional to the current, withthe constant of proportionality , known as the resistance . Resistance has units of ohms, denoted by , named for the German electrical scientist Georg Ohm . Sometimes, the v-i relation for the resistor is written , with , the conductance , equal to . Conductance has units of Siemens (S), and is named for theGerman electronics industrialist Werner von Siemens .
When resistance is positive, as it is in most cases, a resistor consumes power. A resistor's instantaneous power consumption can be written one of two ways.
As the resistance approaches infinity, we have what is known as an open circuit : No current flows but a non-zero voltage can appear across the open circuit. As theresistance becomes zero, the voltage goes to zero for a non-zero current flow. This situation corresponds to a short circuit . A superconductor physically realizes a short circuit.

The capacitor stores charge and the relationship between the charge stored and the resultant voltage is . The constant of proportionality, thecapacitance, has units of farads (F), and is named for the English experimental physicist Michael Faraday . As current is the rate of change of charge,the v-i relation can be expressed in differential or integral form.

The inductor stores magnetic flux, with larger valuedinductors capable of storing more flux. Inductance has units of henries (H), and is named for the American physicist Joseph Henry . The differential and integral forms of the inductor's v-i relation are
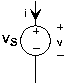

Sources of voltage and current are also circuit elements, butthey are not linear in the strict sense of linear systems. For example, the voltage source's v-i relation is regardless of what the current might be. As for the current source, regardless of the voltage. Another name for a constant-valued voltage source is a battery, and can be purchased in anysupermarket. Current sources, on the other hand, are much harder to acquire; we'll learn why later.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?