| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
“In the last ten years we have come to realize humans are more like worms than we ever imagined.”Bruce Alberts, American scientist and editor of Science magazine
The use of a simple nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans , as a model system for developmental biology has indeed revealed many similarities between that simple creature and ourselves. The animal phyla of this and subsequent modules are triploblastic (i.e., have THREE primary germ layers, ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm in the embryo). They have an embryonic mesoderm sandwiched between the ectoderm and endoderm. Most of these phyla are also bilaterally symmetrical, meaning that a longitudinal section will divide them into right and left sides that are mirror images of each other. Associated with bilateralism is the beginning of cephalization , the evolution of a concentration of nervous tissues and sensory organs in the head of the organism, which is where the organism first encounters its environment.
The flatworms are acoelomate organisms that include free-living and parasitic forms. The nematodes, or roundworms, possess a pseudocoelom and consist of both free-living and parasitic forms. Finally, the arthropods, one of the most successful taxonomic groups on the planet, are coelomate organisms with a hard exoskeleton and jointed appendages.
Most flatworms are parasitic, including important parasites of humans. Free-living species of flatworms are predators or scavengers, whereas parasitic forms feed from the tissues of their hosts. Digestion is extracellular, with enzymes secreted into the gut interior by cells lining the tract, and digested materials taken into the same cells by phagocytosis. One group, the cestodes, does not have a digestive system, because their parasitic lifestyle and the environment in which they live (suspended within the digestive cavity of their host) allows them to absorb nutrients directly across their body wall. Flatworms have an excretory system with a network of tubules throughout the body that open to the environment and nearby flame cells, whose cilia beat to direct waste fluids concentrated in the tubules out of the body. The system is responsible for regulation of dissolved salts and excretion of nitrogenous wastes. The nervous system consists of a pair of nerve cords running the length of the body with connections between them and a large ganglion or concentration of nerve cells at the anterior end of the worm; here, there may also be a concentration of photosensory and chemosensory cells ( [link] ).
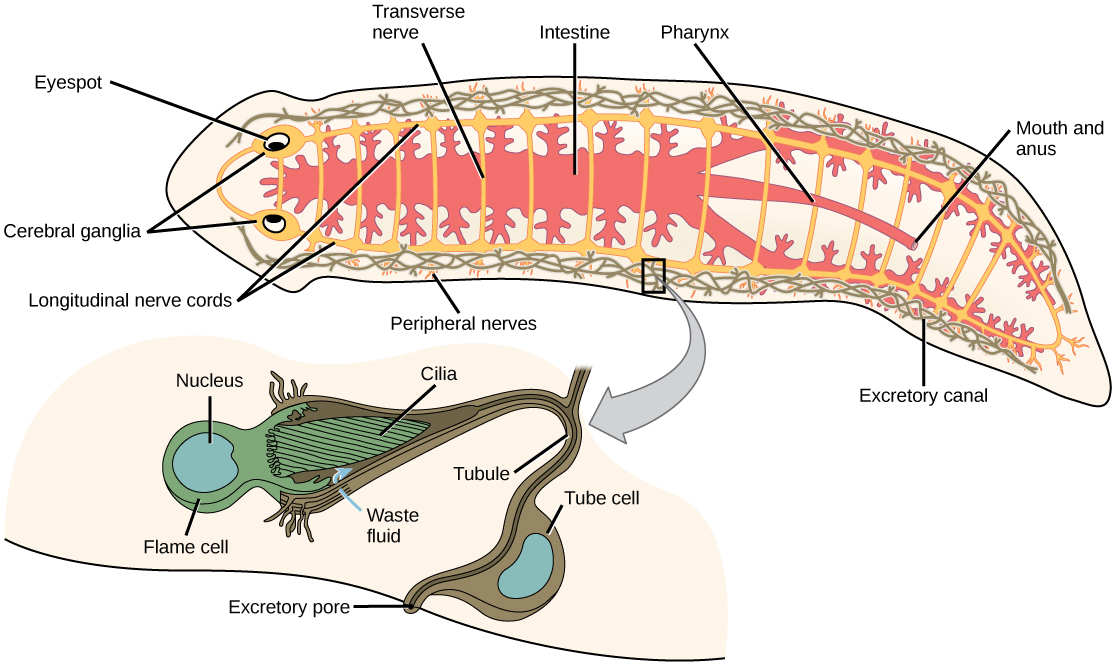
Since there is no circulatory or respiratory system, gas and nutrient exchange is dependent on diffusion and intercellular junctions. This necessarily limits the thickness of the body in these organisms, constraining them to be “flat” worms. Most flatworm species are monoecious (hermaphroditic, possessing both sets of sex organs), and fertilization is typically internal. Asexual reproduction is common in some groups in which an entire organism can be regenerated from just a part of itself.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?